角膜損傷是導致角膜瘢痕形成��,影響角膜透明性和功能的常見原因��,目前臨床需通過角膜移植進行角膜重建��。中山大學中山眼科中心袁進教授和材料科學與工程學院白瑩副教授在科愛出版創(chuàng)辦的期刊 Bioactive Materials 上聯(lián)合發(fā)表研究文章:通過構建互不競爭雙交聯(lián)天然聚合物互穿網(wǎng)絡��,研發(fā)透明度高��、良好組織粘附性和細胞相容性的復合水凝膠��,促進角膜上皮和基質再生��,抑制瘢痕形成��,重建透明角膜��。
1��、研究內容簡介
角膜移植雖然是角膜損傷功能重建的有效方法��,但是供體緊缺仍然是制約角膜復明手術開展的瓶頸��,且供體角膜植片需要通過縫合固定��,不僅會帶來散光��,而且存在如新生血管��、縫線感染等諸多并發(fā)癥��。針對局灶性的角膜損傷采用可原位形成組織粘附性和促再生能力的透明水凝膠進行修復成為新的研究方向��。
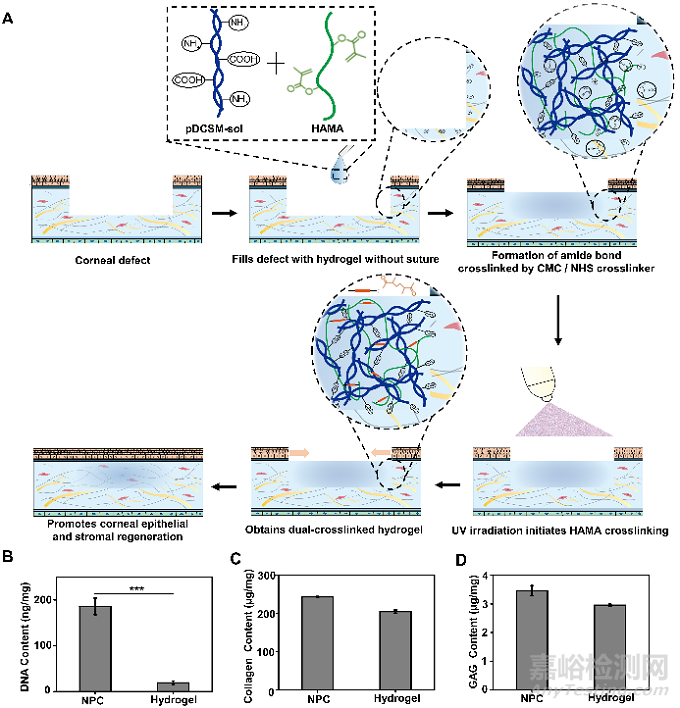
豬來源的去細胞角膜基質水凝膠(pDCSM-G)來源廣��、可注射��。它保留角膜組織中的活性成分��,相比單一組分的水凝膠��,能夠更好模擬原生組織微環(huán)境。但pDCSM-G的力學強度較弱��、降解很快��,無法作為長期有效的角膜修復材料��。為了提高pDCSM-G的力學強度和抗降解性能��,課題組選用CMC/NHS作為pDCSM-G的交聯(lián)劑��,并通過引入可光交聯(lián)的甲基丙烯?�;该髻|酸(HAMA)得到雙交聯(lián)��、雙網(wǎng)絡復合水凝膠��,實現(xiàn)無縫合地快速密封不同形狀和大小的角膜缺損��,并且可以促進角膜再上皮化及基質再生��。
Fig. 1. Application, synthesis, and biomolecular compositions of hydrogels. (A) Schematic illustrations of the hybrid hydrogel applied onto corneal defect in situ for long-term regenerative repair. Quantitative analysis of the (B) DNA, (C) collagen, and (D) GAG contents in the NPCs and those retained in the pDCSM-G, respectively. (***, P<0.001).
雙交聯(lián)復合水凝膠具有理想的光學特性及結構穩(wěn)定性��,其透光率在可見光范圍內超過80%��。優(yōu)選成分比例(C3H1)的復合水凝膠在PBS溶液中幾乎不發(fā)生溶脹��,并且光交聯(lián)HAMA組分的引入賦予該水凝膠較好的抗酶解特性��。
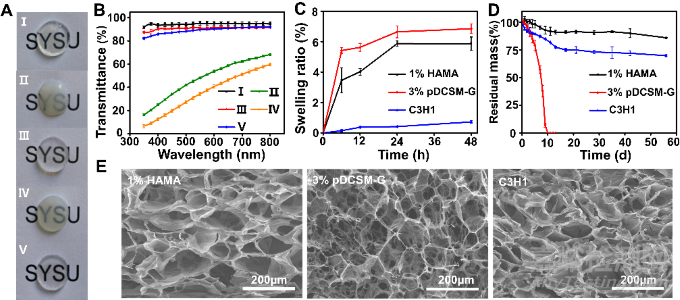
Fig. 2. Optical, swelling, degradation, and microscopic characterizations of the hydrogels. (A) Photographs of the prepared hydrogel specimens (thickness ~ 1 mm) placed on an "SYSU"-labelled paper. The five hydrogel specimens were, (I) photocrosslinked 1% HAMA, (II) physically crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G without CMC/NHS at 37°C, (III) CMC/NHS crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G, (IV) photocrosslinked C3H1 hybrid hydrogel without CMC/NHS at 37°C, and (V) dual-crosslinked C3H1 hydrogel. (B) Light transmittance of the abovementioned five hydrogel specimens on visible light spectrum. (C) Swelling ratios of the photocrosslinked 1% HAMA, CMC/NHS crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G, and dual-crosslinked C3H1 hydrogels when immersed in PBS solution at 37°C in PBS solution within two days, respectively. (D) Long-term degradation behavior of the photocrosslinked 1% HAMA, CMC/NHS crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G, and dual-crosslinked C3H1 hydrogels in 5U/mL collagenase type I solution at 37°C within 60 days, respectively. (E) SEM micrographs of the lyophilized photocrosslinked 1% HAMA, CMC/NHS crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G, and dual-crosslinked C3H1 hydrogels.
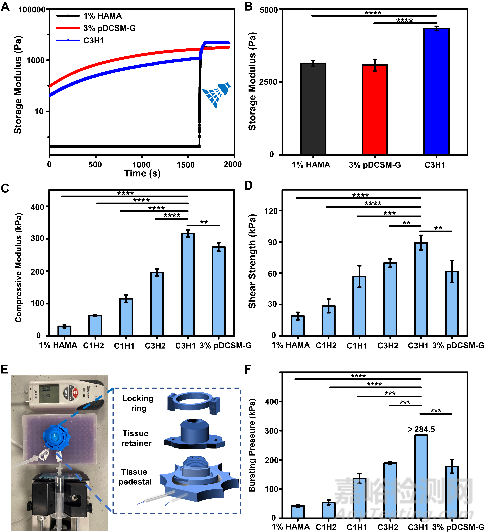
在水凝膠力學性能測試中��,流變測試顯示該復合水凝膠結合了pDCSM-G和HAMA水凝膠的成膠特性��。優(yōu)選成分比例(C3H1)的復合水凝膠擁有最佳的抗形變性能和組織粘附性��,在離體豬角膜的壓力測試中��,它可承受超過284.5mmHg的眼內壓��。這些性質將有利于復合水凝膠在無縫合情況下長期穩(wěn)定地黏附在基質植床上��。
Fig. 3. Mechanical characterizations of the chemically crosslinked hydrogels. (A) Rheological characterization of the photocrosslinked 1% HAMA, CMC/NHS crosslinked 3% pDCSM-G, and dual-crosslinked C3H1 hydrogel before and after light exposure. (B) storage moduli of the 1% HAMA, 3% pDCSM-G, and C3H1 hydrogels after chemical crosslinking, characterized by rheometry. (C) Compressive moduli of the hydrogels with different compositions of HAMA and pDCSM-G. (D) Shear strength of the hydrogels with different compositions of HAMA and pDCSM-G. (E) Photograph of the artificial anterior chamber device used for bursting pressure tests. (F) Averaged bursting pressures of the hydrogels with different compositions of HAMA and pDCSM-G. (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001)
體外細胞培養(yǎng)證明:復合水凝膠無細胞毒性��,有利于角膜細胞的黏附��、存活和增殖��,且能夠幫助維持角膜基質細胞的穩(wěn)定型��,減少角膜基質瘢痕形成��。
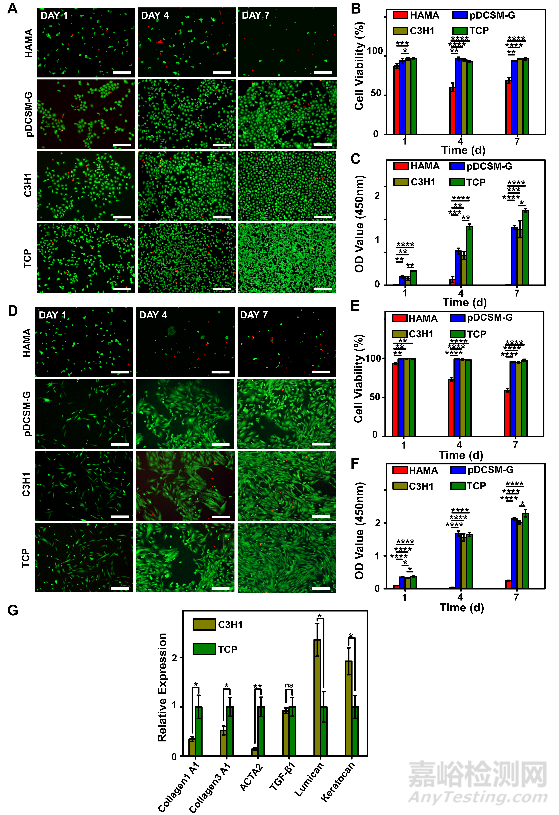
Fig. 4. Corneal epithelial cells and corneal stromal cells cultured on the HAMA, pDCSM-G, C3H1 hydrogels, and TCP. (A) Live/Dead staining of corneal epithelial cells cultured on 1% HAMA, 3% pDCSM-G, C3H1 hydrogel, and TCP for 1, 4, and 7 days, respectively. Scale bars = 200 μm. (B) Quantification of the corneal epithelial cells viability on hydrogels and TCP characterized by Live/Dead assay. (C) CCK-8 assay of the cultured corneal epithelial cells after 1, 4, and 7 days. (D) Live/Dead staining of corneal stromal cells cultured on 1% HAMA, 3% pDCSM-G, C3H1 hydrogel, and TCP for 1, 4, and 7 days. Scale bars = 200 μm. (E) Quantification of the corneal stromal cells viability on hydrogels and TCP characterized by Live/Dead assay. (F) CCK-8 assay of the cultured corneal stroma cells after 1, 4, and 7 days. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of the relative mRNA expression levels of Collagen 1A1, Collagen 3A1, ACTA2, TGF-β1, lumican, and keratocan in the rabbit corneal stromal cells after culturing on the C3H1 hydrogel and TCP for four days. (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001)
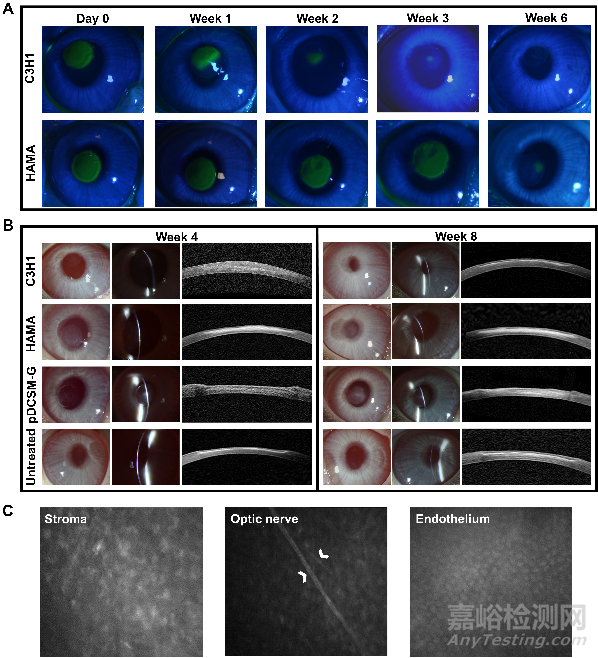
在新西蘭大白兔基質缺損模型中��,該復合水凝膠能夠簡單快速地被注射到基質缺損處,通過自發(fā)的CMC/NHS交聯(lián)劑交聯(lián)和HAMA光引發(fā)成膠��,可以無縫合��、無縫隙地停留于缺損處��,展示出操作的實用性和便捷性��。裂隙燈和AS-OCT結果顯示��,剛填充后的水凝膠能夠與基質植床緊密貼合��,角膜厚度和曲率得到一定的恢復��。
Fig. 5. In vivo application of the hydrogels onto rabbit corneal defects. (A) Procedure of hydrogel injection onto the corneal defect. Representative slit lamp photographs (left) and AS-OCT images (right) after hydrogel treatments using (B) C3H1 hydrogel, (C) 1% HAMA hydrogel, and (D) 3% pDCSM-G, respectively.
原位植入八周后��,填充復合水凝膠的實驗眼在修復前期能夠實現(xiàn)缺損區(qū)域的再上皮化��,角膜保持良好的透明度和角膜弧度��,沒有明顯的炎癥反應和瘢痕生成��。復合水凝膠的填充不會對角膜神經(jīng)��、基質層或內皮層產生不利影響��。其修復效果明顯地好于無法實現(xiàn)快速再上皮化的HAMA組和過快降解的pDCSM-G組��,這兩組的實驗眼均有明顯的基質瘢痕形成��。
Fig. 6. Postoperative observation of the hydrogel treated corneas. (A) Representative photographs of cobalt blue with fluorescein staining in the rabbit experimental eyes filled with C3H1 and 1% HAMA hydrogels at different time points. The green area in the central cornea indicates the epithelial defect. (B) Representative slit lamp and AS-OCT images of the experimental eyes filled with C3H1 hydrogel, 1% HAMA hydrogel, 3% pDCSM-G, and the untreated eyes 4 and 8 weeks after surgery. (C) Confocal micrographs of the corneal stroma, optic nerve, and endothelium in the C3H1-hydrogel-filled cornea 8 weeks post-operation. White arrows point at the optic nerves of the posterior stroma.
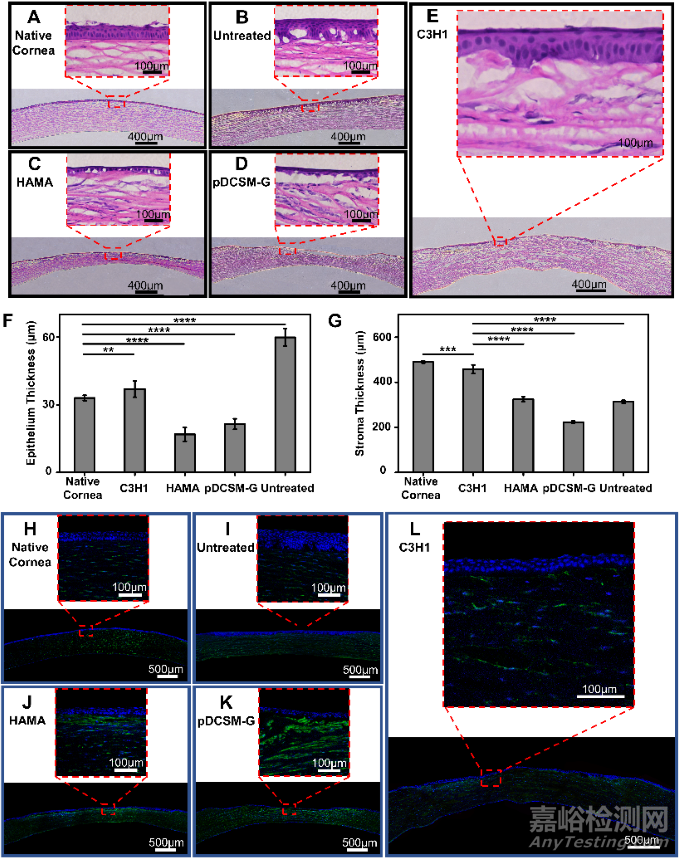
在所有實驗組中��,復合水凝膠在填充至角膜缺損處八周后��,得到最接近正常健康角膜(native cornea)的上皮層和基質層厚度��,基質排列有序��,厚度得到恢復��。與之相比��,HAMA組和pDCSM-G組的缺損處均只生成了單層的上皮細胞層��,有明顯的基質缺損存在��。無處理組則伴隨有明顯的上皮肥大現(xiàn)象��,基質缺損明顯��。免疫熒光染色結果表明,復合水凝膠組的α-SMA的表達顯著低于HAMA組和pDCSM-G組��,意味著更少的基質瘢痕��。因此��,復合水凝膠經(jīng)缺損處無縫合填充后��,表現(xiàn)出更為理想的功能性修復效果和促進角膜再生能力��。
Fig. 7. Histological analysis of the hydrogel treated rabbit corneas eight weeks post-operation. Representative H&E images of (A) native corneas without defect, (B) corneas with untreated defect, and the defected corneas filled with (C) 1% HAMA hydrogel, (D) 3% pDCSM-G, and (E) C3H1 hydrogel. Quantification of (F) epithelium thickness and (G) stroma thickness according to the results from H&E staining. Representative images of immunofluorescence stained (H) native corneas without defect, (I) corneas with untreated defect, and the defected corneas filled with (J) 1% HAMA hydrogel, (K) 3% pDCSM-G, and (L) C3H1 hydrogel, using biomarkers α-SMA (green) and DAPI (blue). (*P<0.05, ****P<0.0001)
綜上所述��,該研究利用互不競爭的雙交聯(lián)體系構建的復合水凝膠展現(xiàn)出良好的理化性能和促再生生物活性��,高透明度��、良好穩(wěn)定性��、可控機械性能及黏附性能��,支持角膜細胞的生長和維持修復表型��。該新型材料可簡便快捷地填充不規(guī)則的角膜缺損��,實現(xiàn)角膜快速再上皮化��,促進角膜基質再生��、減少角膜瘢痕��,表現(xiàn)出良好的功能性修復效果和促進角膜再生能力��,為角膜創(chuàng)傷修復的治療提供了新的干預模式��。