近期�,德國亥姆霍茲中心金屬生物材料研究所研究員Regine Willumeit-Römer在科愛創(chuàng)辦的期刊Bioactive Materials發(fā)表文章。腫瘤細(xì)胞轉(zhuǎn)移是導(dǎo)致癌癥病人死亡的主要原因之一��。近期����,有研究表明含Mg的材料具有抗腫瘤活性。本研究主要探索了含鎂材料在腫瘤轉(zhuǎn)移不同階段中的作用,包括腫瘤細(xì)胞遷移����、侵襲及腫瘤相關(guān)血管生成。實驗證明Mg和Mg-6Ag材料均可有效降低骨肉瘤細(xì)胞遷移和侵襲能力����,并在乏氧環(huán)境中減少腫瘤相關(guān)血管的生成。
引言
“癌癥轉(zhuǎn)移”是指原發(fā)灶的腫瘤細(xì)胞在遠(yuǎn)處形成新的繼發(fā)性腫瘤��,極大降低了癌癥患者的治愈率和生存率�,因癌細(xì)胞轉(zhuǎn)移而死亡的比率占癌癥死亡率的90%以上?;熀头暖熗ǔS糜谥委熌[瘤原發(fā)部位殘留癌細(xì)胞的擴散,但僅對少數(shù)患者有效����,且副作用明顯。因此��,需要新的局部治療策略抑制腫瘤細(xì)胞擴散����,以提高癌癥治療的成功率和患者生命質(zhì)量。近期����,研究表明一種可降解的含鎂的材料表現(xiàn)出明顯的腫瘤細(xì)胞毒性��,且具有良好的生物相容性��,因此����,可作為載藥體系遞送抗腫瘤活性藥物��。該材料的降解速率可改變腫瘤細(xì)胞微環(huán)境�,如pH值��、滲透壓����、氫氣含量等,從而抑制腫瘤細(xì)胞生長��。當(dāng)含鎂材料中引入銀(Ag)或其他金屬元素會改變材料的降解率和生物效應(yīng)��,如加入Ag可增加該材料的抗菌活性�。此前,研究報道了補充Mg2+在腫瘤發(fā)生發(fā)展中的雙面性��,既能促進早期腫瘤的生長,也能抑制晚期實體瘤的侵襲和轉(zhuǎn)移�。然而,含鎂材料是否具有相同的抗腫瘤活性尚未被研究����。本研究著重探索了含鎂材料對腫瘤相關(guān)血管生成、腫瘤侵襲和轉(zhuǎn)移的作用����。
在臨床上,骨肉瘤診斷表明有15-20%的轉(zhuǎn)移率��,伴隨著高死亡率和嚴(yán)重并發(fā)癥��。腫瘤細(xì)胞的轉(zhuǎn)移過程伴隨著上皮間充質(zhì)轉(zhuǎn)化(EMT)��,E-鈣粘素(E-cadherin)蛋白下調(diào)�,及波形蛋白(vimentin)和基質(zhì)金屬蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases, MMP)的上調(diào)。在腫瘤微環(huán)境中�,癌細(xì)胞與癌旁組織細(xì)胞發(fā)生密切的信號交流以誘導(dǎo)腫瘤細(xì)胞的持續(xù)轉(zhuǎn)移,例如成纖維細(xì)胞和巨噬細(xì)胞��。腫瘤細(xì)胞經(jīng)常利用癌旁組織釋放的金屬蛋白酶MMP-2和MMP-9來降解癌細(xì)胞周圍的基質(zhì)����,促進腫瘤細(xì)胞進入到血管中�,隨血液循環(huán)到達(dá)新的部位產(chǎn)生繼發(fā)性腫瘤����。惡性腫瘤快速的增殖需要血管運輸大量的氧氣和營養(yǎng)物質(zhì),當(dāng)腫瘤中心區(qū)域缺氧(O2<3%)且營養(yǎng)不良時�,就會導(dǎo)致腫瘤血管異質(zhì)性。研究表明����,血管內(nèi)皮生長因子(vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF)是血管生成最重要的因子之一,幾乎參與了血管生成的所有步驟�。排列在腫瘤血管壁上的內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞之間間隙增大,有利于腫瘤細(xì)胞滲透到血管內(nèi)��,同時內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞也會增殖和遷移以形成性的腫瘤血管�,并與新的內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞發(fā)生連接(如圖1所示)��。本研究內(nèi)容表明�,Mg2+可顯著影響骨肉瘤細(xì)胞的遷移和侵襲,并改善腫瘤血管異質(zhì)性�。
圖1 常規(guī)、聚乙二醇化�、靶向和多功能脂質(zhì)體的簡化表示
1. 鎂基材料減少了癌細(xì)胞的遷移和侵襲
將骨肉瘤細(xì)胞(Saos-eGFP)和成纖維細(xì)胞單獨或共同接種于細(xì)胞培養(yǎng)皿或覆蓋了Mg或Mg-Ag材料的培養(yǎng)皿中培養(yǎng)0-72 h。通過劃痕實驗觀察不同細(xì)胞在不同培養(yǎng)環(huán)境中的遷移能力�。如圖2所示�,當(dāng)成纖維細(xì)胞與骨肉瘤細(xì)胞共同存在時��,Mg或Mg-Ag材料可顯著抑制細(xì)胞的遷移����。當(dāng)單獨培養(yǎng)細(xì)胞時,Mg或Mg-Ag材料也能明顯抑制癌細(xì)胞的遷移����,但抑制成纖維細(xì)胞遷移的能力下降。
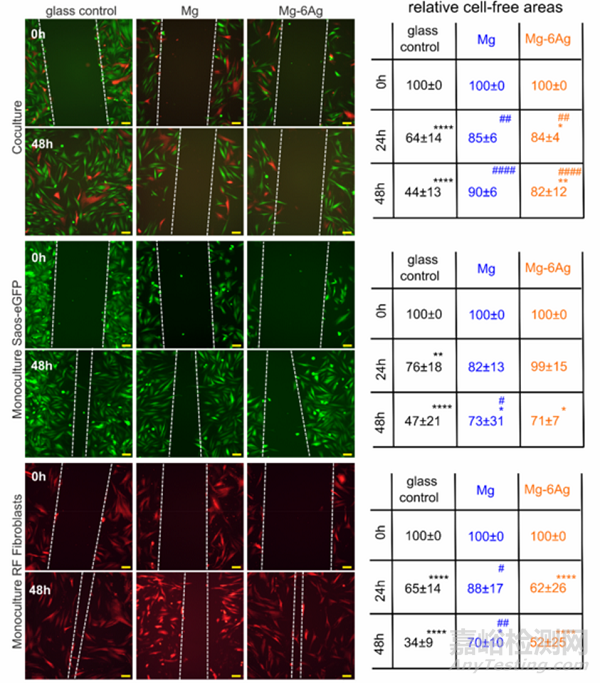
Fig. 2. Cell migration influenced by Mg and Mg–6Ag under normoxia. Microscopic images of Saos-eGFP (green) and RF Fibroblasts (red) in coculture or monocultures with the initial wound (0 h) and after 48 h. The white dotted lines symbolize the cell fronts. Scale bar is 100 μm. The cell-free areas after 24 h and 48 h werequantified in relation to the initial cell-free area. Relative cell-free areas are shown as the mean ± SD from two experiments with two samples and three randomlychosen positions (n = 12). Statistics: two-way ANOVA (Mg, Mg–6Ag compared to glass control = #; 24 h, 48 h compared to 0 h = *) with Tukey’s multiplecomparison test. One symbol = p < 0.05; two symbols = p < 0.01; three symbols p < 0.001; four symbols = p < 0.0001.
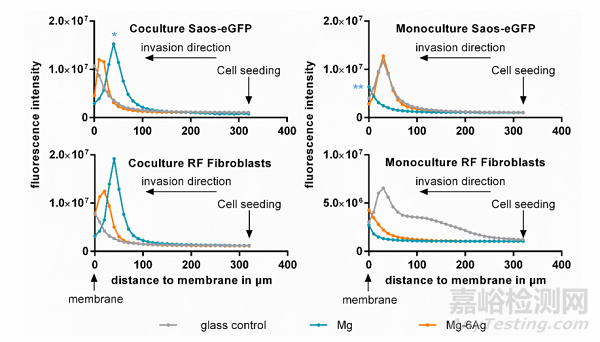
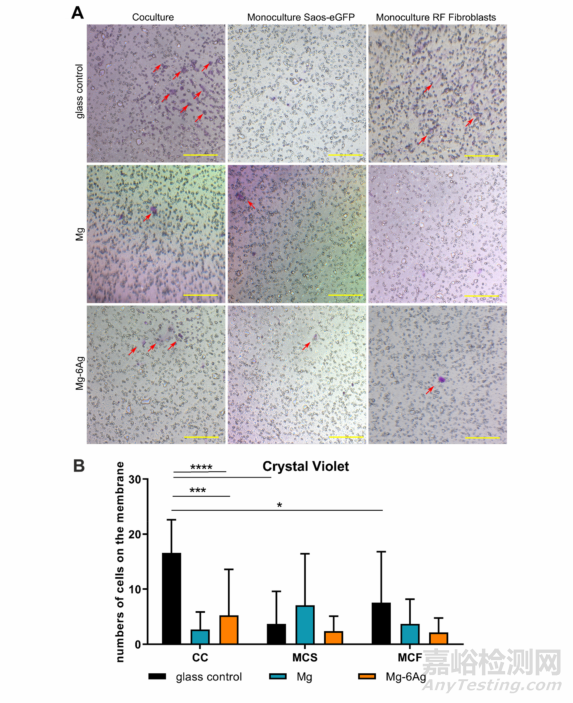
此外��,為研究含鎂材料對癌細(xì)胞侵襲能力的影響����,作者將骨肉瘤細(xì)胞(Saos-eGFP)和成纖維細(xì)胞單獨或共同接種于帶有ECM凝膠的小室中,底部加入細(xì)胞培養(yǎng)基或經(jīng)過Mg或Mg-Ag材料處理的培養(yǎng)基����,通過檢測細(xì)胞向下侵襲的熒光強度來代表細(xì)胞的侵襲能力。圖3表明��,骨肉瘤細(xì)胞和成纖維細(xì)胞共同接種于含Mg材料或Mg-Ag材料的轉(zhuǎn)移小室中�,兩種細(xì)胞的侵襲能力均明顯降低;但兩種細(xì)胞單獨與含Mg材料或Mg-Ag材料共培養(yǎng)時����,細(xì)胞的侵襲能力與對照組相比稍有增加�。圖4對圖三中穿過ECM的細(xì)胞進行結(jié)晶紫染色�,并得出一致結(jié)論。
Fig. 3. Cell invasion influenced by Mg and Mg–6Ag. Cells invaded through an ECM mimetic gel layer from the point of cell seeding (320 μm) to the membrane (0μm). Fluorescence intensities of representative z-stack (10 μm steps) images are shown. Statistics: ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test(n = 12); * = p < 0.01, ** = p < 0.01.
Fig. 4. Visualization of invasive cells. (A) Cells that invaded the ECM mimetic gel layer and crossed the membrane were stained with crystal violet. Red arrows onrepresentative images indicate invaded cells, which were quantified (red numbers). Scale bar is 100 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of images. Statistics: two-wayANOVA (Mg, Mg–6Ag compared to glass control = *) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (n = 12). * = p < 0.05; *** = p < 0.001; **** = p < 0.0001.
綜上��,骨肉瘤細(xì)胞和成纖維細(xì)胞與含鎂材料共孵育時�,骨肉瘤細(xì)胞的遷移和侵襲能力均被明顯抑制,但骨肉瘤細(xì)胞單獨與含鎂材料共培養(yǎng)后��,癌細(xì)胞的遷移和侵襲能力并未下降甚至稍有增加�。
2. 含鎂材料能促進MMP-2、MMP-9和TIMP-1的釋放
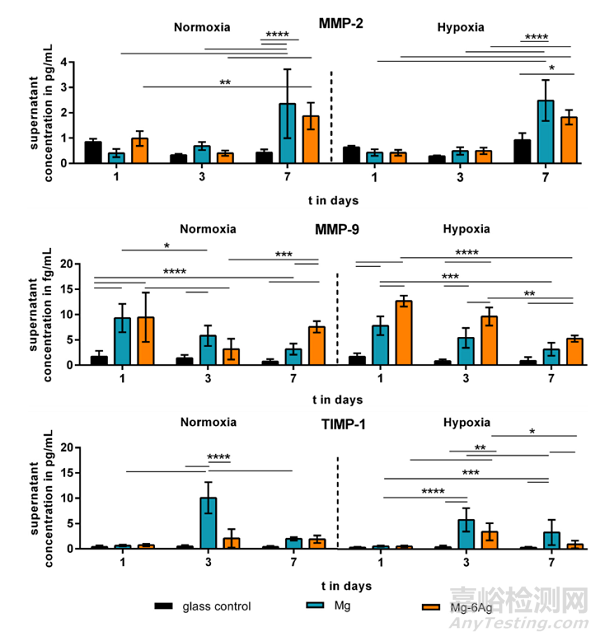
腫瘤組織中高水平的金屬蛋白酶會導(dǎo)致ECM降解����,促進單個腫瘤細(xì)胞遷移并侵襲進入到血管中。圖5顯示Mg或Mg-Ag材料共培養(yǎng)腫瘤細(xì)胞會促進MMP-2����、MMP-和TIMP-1分泌增加�,共培養(yǎng)7天后,MMP-2的分泌量是對照組的2-3倍�;MMP-9在含鎂材料的共培養(yǎng)條件下也顯著增加,但隨共培養(yǎng)的時間呈下降趨勢�;而TIMP-1僅在第三天有明顯增加�,且Mg共培養(yǎng)的效果優(yōu)于Mg-Ag��。
Fig. 5. The impact of Mg-based materials onmetastases-associated cytokine release. MMP-2,MMP-9 and TIMP-1 was quantified in the supernatant of migrating cells of the coculture and normalized to the cell numbers. Normalized cytokineconcentrations are shown as the mean ± SD from twoexperiments with two samples in duplicates (n = 12).Statistics: two-way ANOVA (materials, time points)with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * = p < 0.05;** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.001; **** = p < 0.0001.
3.含鎂材料減少腫瘤血管生成
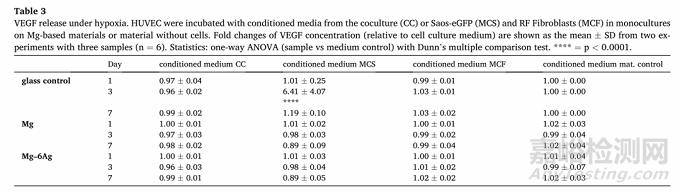
用HUVEC間接模型研究癌癥誘導(dǎo)血管生成��。首先�,如圖6所示,普通培養(yǎng)基中Mg2+的濃度約為0.8 mM��,實驗組培養(yǎng)基分別加入含可降解的Mg和Mg-Ag材料����。隨與細(xì)胞共孵育時間的增加,培養(yǎng)基中游離的Mg2+濃度逐漸升高到3-6 mM����,且Mg2+的釋放與氧氣濃度和孵育細(xì)胞無關(guān)。研究表明�,腫瘤相關(guān)血管生成是由ECM的降解內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞的上皮間質(zhì)轉(zhuǎn)化導(dǎo)致的。圖7探索了含鎂材料和不含鎂材料條件對人臍靜脈內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞(HUVEC)的影響����。常氧條件下,第3-7天內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞間連接通透性明顯增加��,而在缺氧條件下改變不明顯。在第7天��,HUVEC與來自對照組的細(xì)胞的條件培養(yǎng)基(CC����、MCS、MCF)孵育時����,其滲透性略高于與含鎂材料的條件培養(yǎng)基共培養(yǎng)組。VEGF是血管生成最重要的介質(zhì)之一�,可形成新血管��。因此�,測量了條件培養(yǎng)基培養(yǎng)HUVEC后的上清液中VEGF濃度(Table 3)��。含鎂材料培養(yǎng)基和對照培養(yǎng)基共培養(yǎng)并未引起明顯不同的VEGF釋放�,相反,HUVEC與低氧條件下對照組的培養(yǎng)基孵育����,可在第3天顯著增加VEGF濃度�。
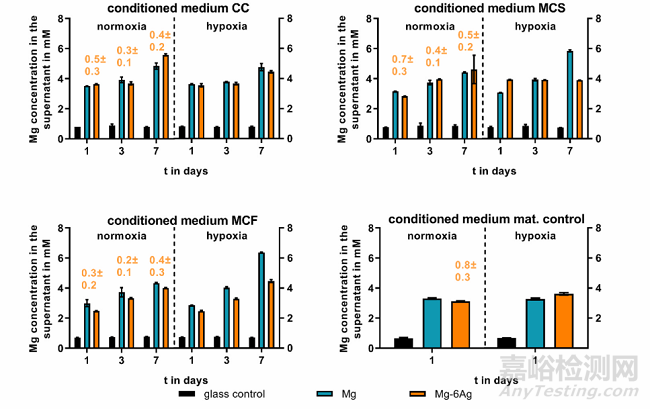
Fig. 6. Supernatant Mg and Ag concentration of conditioned media. Saos-eGFP and RF Fibroblasts were seeded as a 1:1 coculture (CC) or monocultures (Saos-eGFP:MCS, RF Fibroblasts: MCF) on Mg, Mg–6Ag or glass (glass control). Furthermore, material without cells served as a mat. control. After one, three and seven days,conditioned medium was harvested, and Mg (in mM) and Ag (orange numbers, in μM) concentration were measured as described previously.
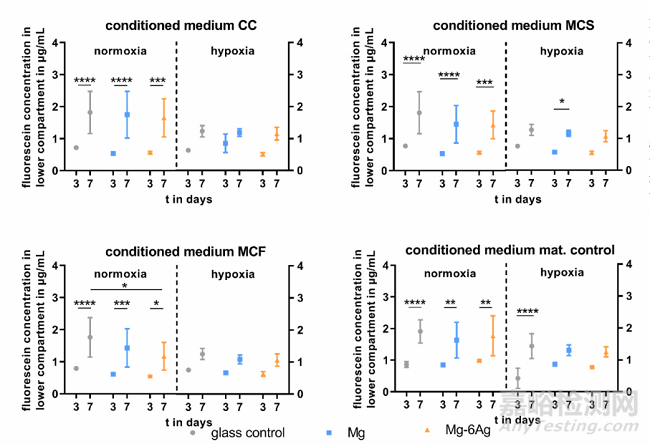
Fig. 7. Endothelial cell layer permeability withdifferent conditioned media. HUVEC were incubatedwith conditioned media from the coculture (CC) orSaos-eGFP (MCS) and RF Fibroblasts (MCF) inmonocultures on Mg-based materials or materialwithout cells. Fluorescein-dextran concentrations (inμg/mL; quantified with a standard curve) are shownas the mean ± SD from two experiments with onetriplicate (n = 6). Statistics: two-way ANOVA (materials, time points) with Tukey’s multiple comparisontest. * = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.001;**** = p < 0.0001.
Table 3VEGF release under hypoxia. HUVEC were incubated with conditioned media from the coculture (CC) or Saos-eGFP (MCS) and RF Fibroblasts (MCF) in monocultureson Mg-based materials or material without cells. Fold changes of VEGF concentration (relative to cell culture medium) are shown as the mean ± SD from two experiments with three samples (n = 6). Statistics: one-way ANOVA (sample vs medium control) with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. **** = p < 0.0001.
4. 含Mg材料影響內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞增殖、遷移和血管再生
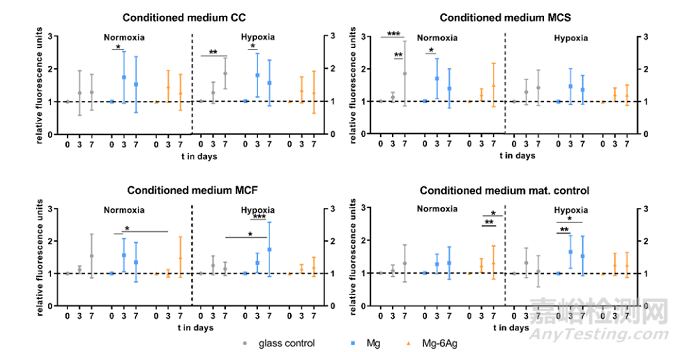
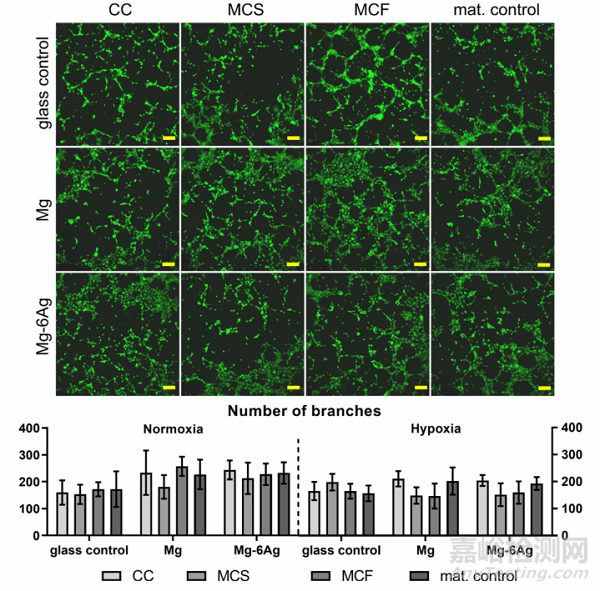
血管生成與內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞增殖和遷移密切相關(guān)����。因此��,可降解鎂基材料條件培養(yǎng)基共培養(yǎng)可監(jiān)測HUVEC的增殖和遷移�。圖8a總結(jié)了直接改變條件培養(yǎng)基第0天、3天和7天后�,由細(xì)胞核染色歸一化熒光強度顯示的HUVEC增殖情況。在所有條件下��,對照組中均觀察到穩(wěn)定的HUVEC增殖����,HUVEC與含Mg (CC, MCS, MCF)培養(yǎng)基共培養(yǎng)基孵育后,內(nèi)皮細(xì)胞增殖從第0天到第3天顯著增加��,隨后在第7天下降����,而在Mg-6Ag培養(yǎng)基中只觀察到少量細(xì)胞數(shù)量變化��。此外��,細(xì)胞劃痕實驗表明含Mg的材料還能明顯減少HUVEC的細(xì)胞遷移��,如圖8b所示����。
Fig. 8a. Endothelial cell proliferation with different conditioned media. HUVEC were incubated with conditioned media from the coculture (CC) or Saos-eGFP (MCS)and RF Fibroblasts (MCF) in monocultures on Mg-based materials or material without cells. Fluorescence intensities (normalized to day 0) are shown as the mean ±SD from two experiments with six triplicates (n = 12). Statistics: two-way ANOVA (materials, time points; compared to day 0) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.* = p < 0.05; ** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.001.
Fig. 8b. Endothelial cell tube formation. Representative pictures of HUVEC capillary structures under normoxia stained with calcein-AM. Scale bar is 100 μm. Imageswere analyzed with the “Angiogenesis analyzer” from ImageJ and branch numbers are shown as the mean ± SD from two experiments with three samples (n = 6).Statistics: two-way ANOVA (materials, time points) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
圖9證明了在常氧(圖9B)和缺氧(圖9C)條件下����,在不同條件介質(zhì)中孵育48 h后HUVEC的遷移(圖9A)����。常氧條件下,含鎂材料并不影響HUVEC的遷移����,但翻樣條件下,可顯著降低HUVEC的遷移�,從而抑制腫瘤相關(guān)血管生成�。
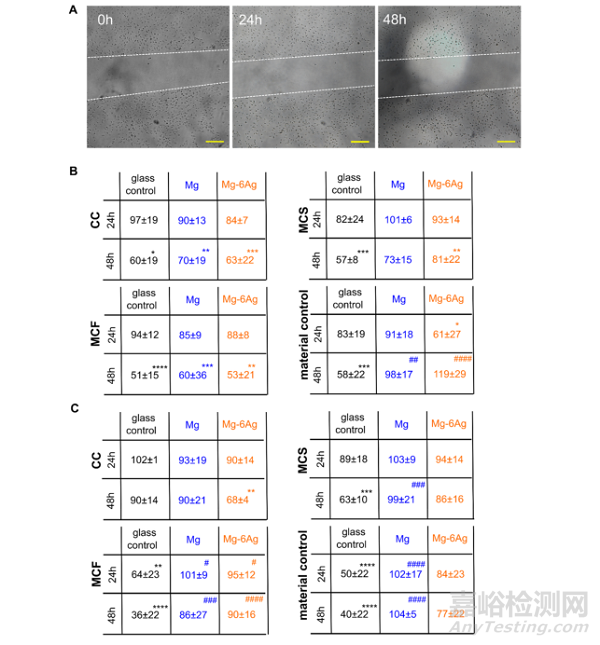
Fig. 9. Endothelial cell migration with different conditioned media. HUVEC were incubated with conditioned media from the coculture (CC) or Saos-eGFP (MCS) andRF Fibroblasts (MCF) in monocultures on Mg-based materials or material without cells. (A) Representative microscopic images of the scratch area in a HUVEC layerwithin 48 h. The white dotted lines symbolize the cell fronts. Scale bar is 100 μm. (B, C) Quantification of the scratch area in relation to the initial cell-free area undernormoxia (B) and hypoxia (C). Relative cell-free areas are shown as the mean ± SD from two experiments with two samples and three chosen positions (n = 12).Statistics: two-way ANOVA (Mg, Mg–6Ag compared to glass control = #; 24 h, 48 h compared to 100% at 0 h = *) with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Onesymbol = p < 0.05; two symbols = p < 0.01; three symbols p < 0.001; four symbols = p < 0.0001.
5. 結(jié)論
研究結(jié)果表明����,含鎂材料是一種具有抗癌活性的可降解材料,在骨肉瘤的發(fā)生和發(fā)展中�,該材料通過抑制癌細(xì)胞的遷移、侵襲和腫瘤相關(guān)血管的生成來減少骨肉瘤轉(zhuǎn)移的發(fā)生率��。然而�,含鎂基材料降解的決定環(huán)境因素包括pH和滲透壓等��。我們的研究僅揭示了緩慢降解的鎂材料對骨肉瘤進展的影響��,而未來的研究應(yīng)使用不同降解率的材料來驗證這些結(jié)果����。
原文信息:Mg-based materials diminish tumor spreading and cancer metastases.
Philipp Globig, Roshani Madurawala, Regine Willumeit-Römer, Fernanda Martini, Elisa Mazzoni, Bérengère J.C. Luthringer-Feyerabend.
Bioactive Materials, 19 (2023) 594-610.