This is an example pharmaceutical development report illustrating how ANDA applicants can move toward implementation of Quality by Design (QbD). The purpose of the example is to illustrate the types of pharmaceutical development studies ANDA applicants may use as they implement QbD in their generic product development and to promote discussion on how OGD would use this information in review.
FDA官網(wǎng)中一個(gè)有關(guān)藥物開發(fā)報(bào)告的實(shí)例�����,用以說(shuō)明ANDA申請(qǐng)人如何實(shí)施質(zhì)量源于設(shè)計(jì)(QbD)�����。 該實(shí)例的目的是說(shuō)明申請(qǐng)人在其仿制藥開發(fā)過(guò)程中實(shí)施QbD時(shí)����,可使用的藥物開發(fā)研究的類型,同時(shí)促進(jìn)探討OGD在審評(píng)中如何使用該信息��。
本文主要概述和分析了參與制劑���,包括參比制劑的臨床�、藥動(dòng)學(xué)�、藥物釋放��、理化性質(zhì)和組分���,為藥物進(jìn)一步開發(fā)積累認(rèn)知。
1.1 Executive Summary 概述
The following pharmaceutical development report summarizes the development of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, a generic version of the reference listed drug (RLD), Brand Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg. The RLD is an immediate release (IR) tablet indicated for the relief of moderate to severe physiological symptoms. We used Quality by Design (QbD) to develop generic acetriptan IR tablets that are therapeutically equivalent to the RLD.
總結(jié)了如下藥物開發(fā)報(bào)告��,開發(fā) 20 mg Acetriptan 片的仿制藥���,一種商品名 20 mg Acetriptan 片的參考目錄藥物(RLD)的仿制藥��。RLD 為速釋(IR)片�����,用于緩解中度至重度生理癥狀���。使用質(zhì)量源于設(shè)計(jì)(QbD)法用以開發(fā)與 RLD 治療等效的 acetriptan IR 片的仿制藥。
Initially, the quality target product profile (QTPP) was defined based on the properties of the drug substance, characterization of the RLD product, and consideration of the RLD label and intended patient population. Identification of critical quality attributes (CQAs) was based on the severity of harm to a patient (safety and efficacy) resulting from failure to meet that quality attribute of the drug product. Our investigation during pharmaceutical development focused on those CQAs that could be impacted by a realistic change to the drug product formulation or manufacturing process. For generic acetriptan tablets, these CQAs included assay, content uniformity, dissolution and degradation products.
明確目標(biāo)藥品的質(zhì)量概況(QTPP)是根據(jù)原料藥的性質(zhì)���,RLD 產(chǎn)品的特性���,并考慮到 RLD 標(biāo)簽和預(yù)定患者人群。關(guān)鍵質(zhì)量屬性(CQAs)的確定是基于由于不符合藥品的質(zhì)量屬性而對(duì)患者造成的傷害嚴(yán)重性(安全性和有效性)��。在藥物開發(fā)中研究集中在那些可能受制劑處方或生產(chǎn)工藝的實(shí)際變動(dòng)而受到影響的CQAs�����。對(duì) acetriptan 片的仿制藥�����,這些 CQAs 包括含量��,含量均勻度�,溶出和降解物。
Acetriptan is a poorly soluble, highly permeable Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) Class II compound. As such, initial efforts focused on developing a dissolution method that would be able to predict in vivo performance. The developed in-house dissolution method uses 900 mL of 0.1 N HCl with 1.0% w/v sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) in USP apparatus 2 stirred at 75 rpm. This method is capable of differentiating between formulations manufactured using different acetriptan particle size distributions (PSD) and predicting their in vivo performance in the pilot bioequivalence (BE) study.
Acetriptan為難溶�,高滲透生物藥劑分類系統(tǒng)(BCS)II類化合物。因此�����,初始工作集中于開發(fā)一種可預(yù)測(cè)體內(nèi)性能的溶出方法���。開發(fā)的溶出方法為在75rpm轉(zhuǎn)速的USP裝置2中����,使用900 mL含1.0% w/v十二烷基硫酸鈉(SLS)的0.1 N HCl溶液。該方法能區(qū)分使用不同 acetriptan粒度分布(PSD)生產(chǎn)的處方并預(yù)測(cè)其在中試生物等效性(BE)研究中的體內(nèi)性能�����。
Risk assessment was used throughout development to identify potentially high risk formulation and process variables and to determine which studies were necessary to achieve product and process understanding in order to develop a control strategy. Each risk assessment was then updated after development to capture the reduced level of risk based on our improved product and process understanding.
在整個(gè)開發(fā)中使用風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評(píng)估以確認(rèn)潛在的高風(fēng)險(xiǎn)處方和工藝變量����,并確定哪些研究是必須的以達(dá)到對(duì)產(chǎn)品和工藝的理解以便開發(fā)一種控制策略。然后基于我們對(duì)產(chǎn)品和工藝改進(jìn)的理 解���,在開發(fā)后更新每個(gè)風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評(píng)估以獲得降低的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)水平����。
For formulation development, an in silico simulation was conducted to evaluate the potential effect of acetriptan PSD on in vivo performance and a d90 of 30 μm or less was selected. Roller compaction (RC) was selected as the granulation method due to the potential for thermal degradation of acetriptan during the drying step of a wet granulation process. The same types of excipients as the RLD product were chosen. Excipient grade selection was based on experience with previously approved ANDA 123456 and ANDA 456123 which both used roller compaction. Initial excipient binary mixture compatibility studies identified a potential interaction between acetriptan and magnesium stearate. However, at levels representative of the final formulation, the interaction was found to be negligible. Furthermore, the potential interaction between acetriptan and magnesium stearate is limited by only including extragranular magnesium stearate.
對(duì)于處方開發(fā)�����,進(jìn)行計(jì)算機(jī)模擬以評(píng)估acetriptan PSD對(duì)體內(nèi)性能的潛在影響�,選擇了d90為30 μm或低于30 μm。選擇碾壓(RC)作為制粒方法由于acetriptan在濕法制粒工藝的干燥步驟中可能發(fā)生熱降解�。選擇與RLD產(chǎn)品相同類型的輔料,輔料級(jí)別的選擇是基于先前批準(zhǔn)的 ANDA 123456和ANDA 456123都使用碾壓的經(jīng)驗(yàn)�。初始輔料二元混合物相容性研究確認(rèn) acetriptan和硬脂酸鎂間有潛在相互作用。但是��,在表示最終處方的濃度下,發(fā)現(xiàn)該相互作用可忽略不計(jì)��。此外���,acetriptan和硬脂酸鎂間的潛在相互作用受僅包括外加硬脂酸鎂的限制。
Two formulation development design of experiments (DOE) were conducted. The first DOE investigated the impact of acetriptan PSD and levels of intragranular lactose, microcrystalline cellulose and croscarmellose sodium on drug product CQAs. The second DOE studied the levels of extragranular talc and magnesium stearate on drug product CQAs. The formulation composition was finalized based on the knowledge gained from these two DOE studies.
進(jìn)行了兩個(gè)處方開發(fā)實(shí)驗(yàn)設(shè)計(jì)(DOE)���。第一個(gè)DOE研究了acetriptan PSD和外加乳糖�,微晶纖維素和交聯(lián)羧甲基纖維素鈉的濃度對(duì)制劑CQAs的影響�����。第二個(gè)DOE研究了外加滑石粉和硬脂酸鎂的濃度對(duì)制劑CQAs的影響���?����;谶@兩個(gè)DOE研究所得的知識(shí)���,確定了處方成分。
An in-line near infrared (NIR) spectrophotometric method was validated and implemented to monitor blend uniformity and to reduce the risk associated with the pre-roller compaction blending and lubrication step. Roller pressure, roller gap and mill screen orifice size were identified as critical process parameters (CPPs) for the roller compaction and integrated milling process step and acceptable ranges were identified through the DOE. Within the ranges studied during development of the final blending and lubrication step, magnesium stearate specific surface area (5.8-10.4 m2/g) and number of revolutions (60-100) did not impact the final product CQAs. During tablet compression, an acceptable range for compression force was identified and force adjustments should be made to accommodate the ribbon relative density (0.68-0.81) variations between batches in order to achieve optimal hardness and dissolution.
驗(yàn)證了在線近紅外(NIR)分光光度法并用于監(jiān)測(cè)混合均勻度和降低與預(yù)碾壓混合和潤(rùn)滑步驟相關(guān)的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)��。軋輥壓力,軋輥間隙和細(xì)篩孔徑確定為碾壓和集成粉碎工藝步驟的關(guān)鍵工藝參數(shù)(CPPs)并通過(guò)DOE確定了可接受范圍�����。在開發(fā)最終混合和潤(rùn)滑步驟中的研究范圍內(nèi)���,硬脂酸鎂比表面積(5.8~10.4 m2/g)和轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)(60~100)不影響最終產(chǎn)品CQAs�����。在壓片中�����,確定了可接受范圍的壓縮力并應(yīng)調(diào)整壓縮力以容納批次間帶狀物相對(duì)密度(0.68~0.81)的變化以便達(dá) 到硬度和溶出的最優(yōu)化���。
Scale-up principles and plans were discussed for scaling up from lab (5.0 kg) to pilot scale (50.0 kg) and then proposed for commercial scale (150.0 kg). A 50.0 kg cGMP exhibit batch was manufactured at pilot scale and demonstrated bioequivalence in the pivotal BE study. The operating ranges for identified CPPs at commercial scale were proposed and will be qualified and continually verified during routine commercial manufacture.
討論了從實(shí)驗(yàn)室規(guī)模(5.0 kg)放大至中試規(guī)模(50.0 kg)的放大原則和計(jì)劃,然后擬定了工業(yè)規(guī) 模(150.0 kg)�。在中試規(guī)模下生產(chǎn)了50.0 kg cGMP申報(bào)批并在關(guān)鍵BE研究中顯示生物等效。工業(yè)規(guī)模下�����,擬定了已確認(rèn)的CPPs操作范圍���,在常規(guī)工藝生產(chǎn)中將進(jìn)行限定并持續(xù)驗(yàn)證��。
Finally, we proposed a control strategy that includes the material attributes and process parameters identified as potentially high risk variables during the initial risk assessments. Our control strategy also includes in-process controls and finished product specifications. The process will bemonitored during the lifecycle of the product and additional knowledge gained will be utilized to make adjustments to the control strategy as appropriate.
最后���,我們提出了控制策略���,包括初始風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評(píng)估中確認(rèn)為潛在高風(fēng)險(xiǎn)變量的物質(zhì)屬性和工藝參數(shù)。將在產(chǎn)品的生命周期中監(jiān)測(cè)工藝并且獲得的額外知識(shí)將用于對(duì)控制策略的適當(dāng)調(diào)整���。
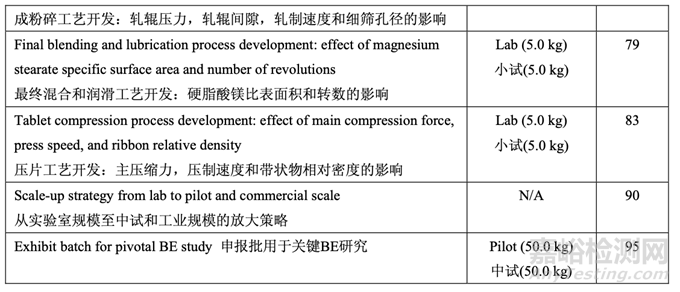
The development time line for Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, is presented in Table 1.
仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的開發(fā)時(shí)間線列于表 1。
Table 1. Development of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, presented in chronological order
表 1 仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的開發(fā)��,以時(shí)間順序排序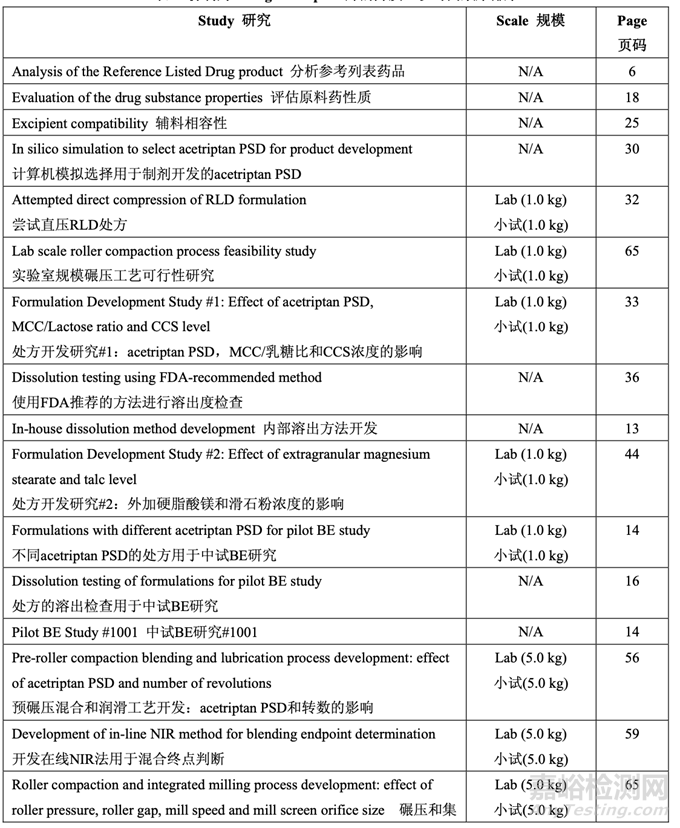
1.2 Analysis of the Reference Listed Drug Product 分析參比制劑
1.2.1 Clinical 臨床
The Reference Listed Drug (RLD) is Brand Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, and was approved in the United States in 2000 (NDA 211168) for therapeutic relief of moderate to severe symptoms. The RLD is an unscored immediate release (IR) tablet with no cosmetic coating. The tablet needs to be swallowed “as is” without any intervention. Thus, the proposed generic product will also be an unscored IR tablet with no cosmetic coating. The maximum daily dose in the label is 40 mg (i.e., one tablet twice per day). A single tablet is taken per dose with or without food. Brand Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, should be swallowed whole with a glass of water.
參比藥品(RLD)為商品名20 mg Acetriptan片���,于2000年在美國(guó)批準(zhǔn)(NDA 211168)用于治療緩解中度至重度癥狀���。RLD為無(wú)刻痕非包衣的速釋(IR)片。需“依現(xiàn)狀”吞下片劑而無(wú)任何 干預(yù)����。因此,擬定仿制藥也是為無(wú)刻痕非包衣IR片�����。標(biāo)簽中的最大日劑量為40 mg (即一日 兩次,每次一片)�。單位劑量的單片可與食物或不與食物服用。商品名20 mg Acetriptan片�����, 應(yīng)用一杯水整片吞服�����。
1.2.2 Pharmacokinetics 藥動(dòng)學(xué)
Acetriptan is well absorbed after oral administration. The median Tmax is 2.5 hours (h) in patients. The mean absolute bioavailability of acetriptan is approximately 40%. The AUC and Cmax of acetriptan are increased by approximately 8% to 12% following oral dosing with a high fat meal. The terminal elimination half-life of acetriptan is approximately 4 hours.
Acetriptan口服后吸收良好�����?�;颊叩钠骄鵗max為2.5小時(shí)����。Acetriptan的平均絕對(duì)生物利用度約 40%。與高脂肪飲食一起服用后��,acetriptan的AUC和Cmax增加了約8%~12%�����。Acetriptan的 末端消除半衰期約4小時(shí)。
1.2.3 Drug Release 藥物釋放
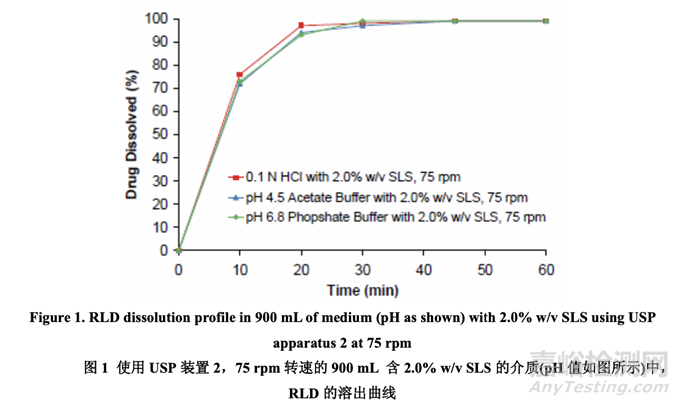
Drug release is usually the rate limiting process for absorption of a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) Class II compound like acetriptan due to its low solubility. Therefore, the dissolution of the RLD tablets was thoroughly evaluated. Initially, the dissolution method recommended in the FDA dissolution methods database for this product was utilized (900 mL of 0.1 N HCl with 2.0% w/v sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) using USP apparatus 2 (paddle) at 75 rpm). The temperature of the dissolution medium was maintained at 37 ± 0.5 °C and the drug concentration was determined using UV spectroscopy at a wavelength of 282 nm. The drug release of RLD tablets was also obtained at different medium pH (pH 4.5 acetate buffer and pH 6.8 phosphate buffer) with 2.0% w/v SLS. As shown in Figure 1, RLD tablets exhibited a very rapid dissolution using the FDA-recommended method without any sensitivity to medium pH.
對(duì)于像acetriptan的生物藥學(xué)分類系統(tǒng)(BCS) II類化合物的吸收���,由于其低溶解度��,藥物釋放通常是速率限制過(guò)程�����。因此���,應(yīng)徹底評(píng)估 RLD 片劑的溶出���。開始���,使用該產(chǎn)品在 FDA 溶出方法數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)中推薦的溶出方法(用 USP 裝置 2(槳法),轉(zhuǎn)速為 75 rpm�,900 mL 含 2.0% w/v 十二烷基硫酸鈉(SLS) 的 0.1 N HCl 溶出介質(zhì))。溶出介質(zhì)的溫度維持在 37 ± 0.5 °C�����,用 UV 分光光度法在 282 nm 波長(zhǎng)處測(cè)定藥物濃度。也得到了在含 2.0% w/v SLS 的不同 pH 值 (pH 4.5 醋酸緩沖液和 pH 6.8 磷酸緩沖液)溶出介質(zhì)的 RLD 片劑的藥物釋放���。如圖 1 所示��,使用 FDA 推薦的方法�����,RLD 片劑顯示出快速溶出����,對(duì)介質(zhì) pH 值不敏感�。
1.2.4 Physicochemical Characterization 理化性質(zhì)
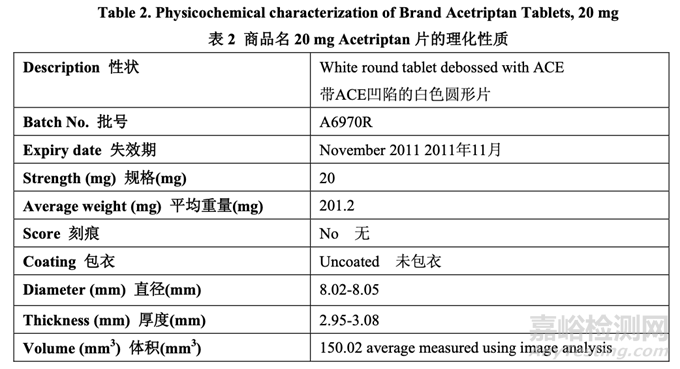
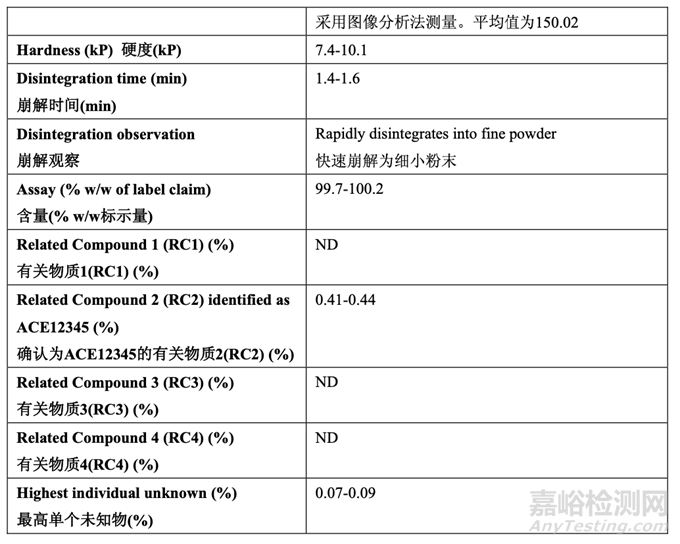
The physicochemical characterization of the RLD tablet is summarized in Table 2. Characterization included determination of the level of ACE12345, a known degradant, in near expiry product.
RLD 片的理化性質(zhì)概述在表 2 中。性質(zhì)包括了測(cè)定 ACE12345���,一種已知降解物��,在臨失效 產(chǎn)品中的濃度���。
1.2.5 Composition 組分
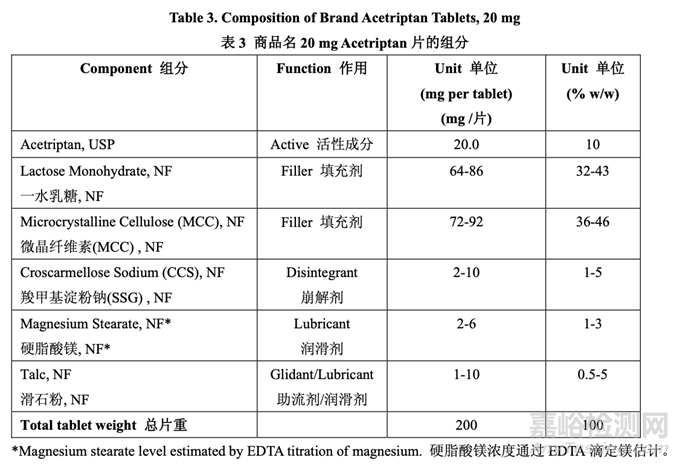
Based on the RLD labeling, patent literature and reverse engineering, Table 3 lists the composition of Brand Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg. The level provided for each excipient is consistent with previous experience and is below the level listed in the inactive ingredient database (IID) for FDA-approved oral solid dosage forms.
基于 RLD 標(biāo)簽,專利文獻(xiàn)和反向工程���,表 3 列出了商品名 20 mg Acetriptan 片的組分��。每個(gè)輔料提供的濃度與之前的經(jīng)驗(yàn)一致��,低于 FDA 批準(zhǔn)的口服固體制劑非活性成分?jǐn)?shù)據(jù)庫(kù)(IID) 所列出的濃度��。
參考文獻(xiàn):
Example QbD IR Tablet Module 3 Quality 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development���,F(xiàn)DA�����,2012.