This is an example pharmaceutical development report illustrating how ANDA applicants can move toward implementation of Quality by Design (QbD). The purpose of the example is to illustrate the types of pharmaceutical development studies ANDA applicants may use as they implement QbD in their generic product development and to promote discussion on how OGD would use this information in review.
FDA官網(wǎng)中一個有關(guān)藥物開發(fā)報告的實例�,用以說明申請人如何實施質(zhì)量源于設計(QbD)。 該實例的目的是說明ANDA申請人在其仿制藥開發(fā)過程中實施QbD時�,可使用的藥物開發(fā)研究的類型,同時促進探討OGD在審評中如何使用該信息�。
本文主要概述了制劑的目標質(zhì)量概況和溶出方法開發(fā)的關(guān)鍵要點����。
1.3 Quality Target Product Profile for the ANDA Product
ANDA藥品的目標藥品的質(zhì)量概況
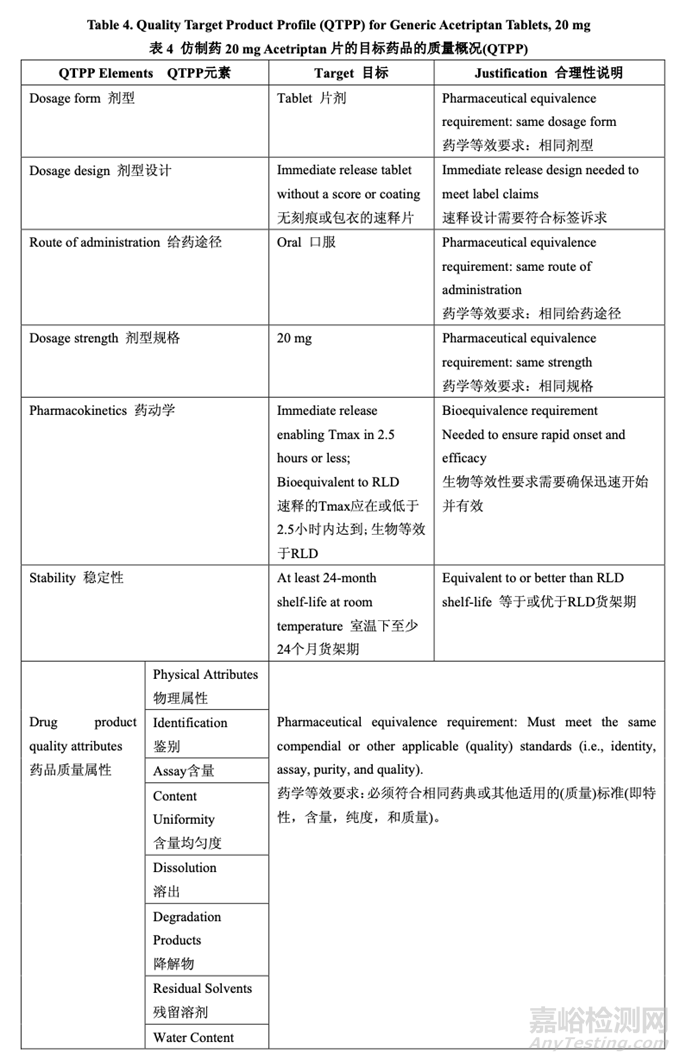
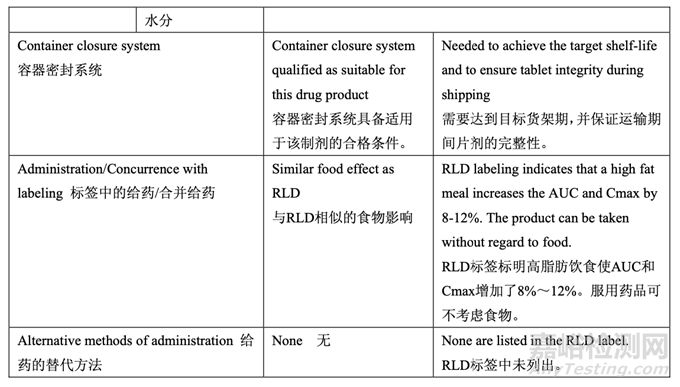
Note to Reader: The quality target product profile (QTPP) is “a prospective summary of thequality characteristics of a drug product that ideally will be achieved to ensure the desired quality, taking into account safety and efficacy of the drug product.” 1 The QTPP is an essential element of a QbD approach and forms the basis of design of the generic product. For ANDAs, the target should be defined early in development based on the properties of the drug substance (DS), characterization of the RLD product and consideration of the RLD label and intended patient population. The QTPP includes all product attributes that are needed to ensure equivalent safety and efficacy to the RLD. This example is for a simple IR tablet; other products would include additional attributes in the QTPP. By beginning with the end in mind, the result of development is a robust formulation and manufacturing process with a control strategy that ensures the performance of the drug product.
致讀者:目標藥品的質(zhì)量概況(QTPP)是“從理論上達到對藥品質(zhì)量特性的前瞻性總結(jié),確保預期的質(zhì)量�,同時兼顧藥品的安全性和有效性“�。
1 QTPP是QbD方法的基本要素并形成仿制藥設計的基礎(chǔ)���。對于ANDAs,應在開發(fā)的早期����,基于藥物(DS)性質(zhì),RLD藥品的特征并兼顧 RLD標簽和預期的患者人口確定目標。QTPP包括需要保證與RLD安全性和有效性等效的所有產(chǎn)品屬性����。該實例適用于單一IR片;其他產(chǎn)品將包括QTPP中的額外屬性���。通過以終為始���, 開發(fā)的結(jié)果是處方穩(wěn)定����,生產(chǎn)工藝的控制策略可確保藥品的性能�。
A critical quality attribute (CQA) is “a physical, chemical, biological, or microbiological property or characteristic that should be within an appropriate limit, range, or distribution to ensure the desired product quality.”1 The identification of a CQA from the QTPP is based on the severity of harm to a patient should the product fall outside the acceptable range for thatattribute.
關(guān)鍵質(zhì)量屬性(CQA)是“物理�,化學,生物學����,或微生物學性質(zhì)或特點���,應在適宜的限度范圍內(nèi),或分布內(nèi)以保證預期的藥品質(zhì)量”�。QTPP中確認CQA是基于該屬性在可接受范圍 外的藥品對患者傷害的嚴重程度。
All quality attributes are target elements of the drug product and should be achieved through a good quality management system as well as appropriate formulation and process design and development. From the perspective of pharmaceutical development, we only investigate the subset of CQAs of the drug product that also have a high potential to be impacted by the formulation and/or process variables. Our investigation culminates in an appropriate control strategy.
所有的質(zhì)量屬性都是藥品的目標元素,應通過良好質(zhì)量管理系統(tǒng)�,適宜的處方和工藝設計及開發(fā)來實現(xiàn)。從藥物開發(fā)的角度來看,我們僅研究也有高度可能受處方和/或工藝變量影響 的藥品 CQAs 的一部分。我們的研究以適宜的控制策略告終�。
Based on the clinical and pharmacokinetic (PK) characteristics as well as the in vitro dissolution and physicochemical characteristics of the RLD, a quality target product profile (QTPP) was defined for Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg (see Table 4).
基于 RLD 的臨床和藥動學(PK)特征及體外溶出和理化性質(zhì)�,確定了仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的目標藥品的質(zhì)量概況(QTPP)(見表 4)。
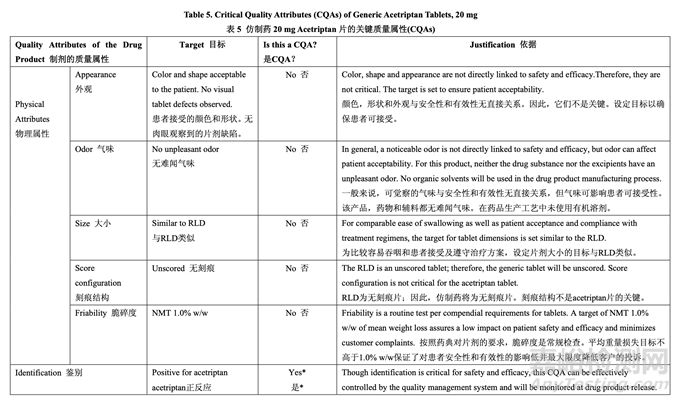
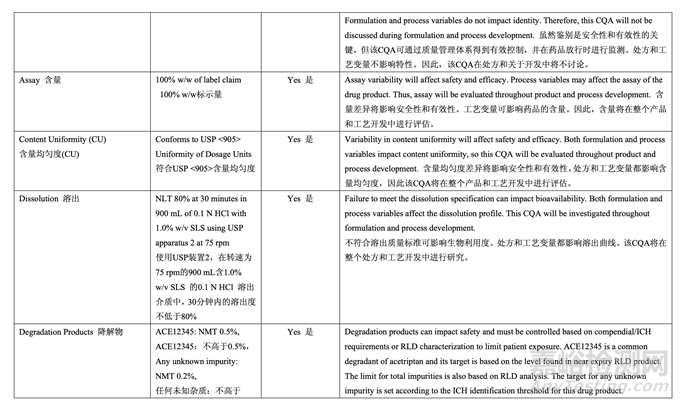
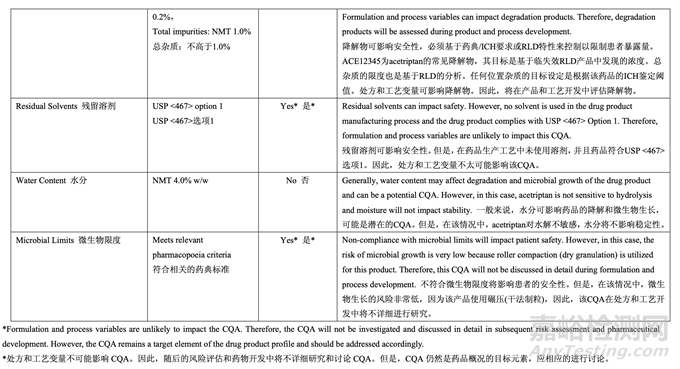
Table 5 summarizes the quality attributes of generic acetriptan tablets and indicates which attributes were classified as drug product critical quality attributes (CQAs). For this product, assay, content uniformity (CU), dissolution and degradation products are identified as the subset of CQAs that have the potential to be impacted by the formulation and/or process variables and, therefore, will be investigated and discussed in detail in subsequent formulation and process development studies.
表 5 概述了仿制藥 acetriptan 片的質(zhì)量屬性,并指出了那些屬性被列為藥品關(guān)鍵質(zhì)量屬性 (CQAs)���。對于該產(chǎn)品����,確定含量����,含量均勻度(CU)���,溶出和降解物為可能受處分和/或工藝變量影響的 CQAs 的一部分�,并因此���,將在隨后的處方和工藝開發(fā)研究中詳細研究并討論�。
On the other hand, CQAs including identity, residual solvents and microbial limits which are unlikely to be impacted by formulation and/or process variables will not be discussed in detail in the pharmaceutical development report. However, these CQAs are still target elements of the QTPP and are ensured through a good pharmaceutical quality system and the control strategy.
另一方面���,藥物開發(fā)報告中不詳細討論不可能受處分和/或工藝變量影響的 CQAs 包括特性�, 殘留溶劑和微生物限度。但是�,這些 CQAs 仍然是 QTPP 的目標元素�,并通過良好藥品質(zhì)量 系統(tǒng)和控制策略得到保證�。
1.4 Dissolution Method Development and Pilot Bioequivalence Studies
溶出方法開發(fā)和中試生物等效性研究
Note to Reader: A pharmaceutical development report should document the selection of the dissolution method used in pharmaceutical development. This method (or methods) may differ from the FDA-recommended dissolution method and the quality control method used for release testing.
藥物開發(fā)報告應記錄藥物開發(fā)中使用的溶出方法的選擇����。該方法(或這些方法)可不同于FDA推薦的溶出方法和用于釋放檢查的質(zhì)量控制方法。
1.4.1 Dissolution Method Development 溶出方法開發(fā)
Acetriptan is a BCS Class II compound displaying poor aqueous solubility (less than 0.015 mg/mL) across the physiological pH range. As such, development of a dissolution method that can act as the best available predictor of equivalent pharmacokinetics to the RLD was pursued to allow assessment of acetriptan tablets manufactured during development. Acetriptan
在整個生理pH值范圍內(nèi)顯示出水溶性差(低于0.015 mg/mL)����,為BCS II類化合物。 因此���,進行一種在預測與RLD藥動學等效方面起最佳作用的溶出方法的開發(fā)���,以允許評估開發(fā)期間acetriptan片的生產(chǎn)�。
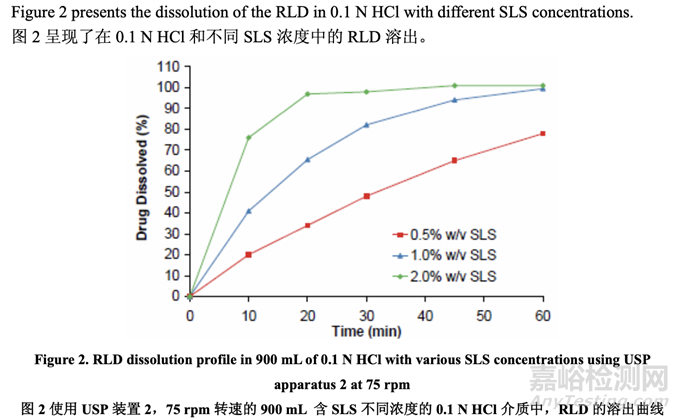
The target is an immediate release product, so dissolution in the stomach and absorption in the upper small intestine is expected suggesting the use of dissolution medium with low pH. Development began with the quality control dissolution method recommended for this product by the FDA: 900 mL of 0.1 N HCl with 2.0% w/v SLS using USP apparatus 2 at 75 rpm. Initial development formulations (Batches 1-11) exhibited rapid dissolution (NLT 90% dissolved in 30 minutes (min)) and were comparable to the RLD. It became a challenge for the team to select the formulations which might perform similarly to the RLD in vivo. The solubility of acetriptan in various media was determined (Table 6) and suggests that the solubility of acetriptan in 0.1 N HCl with 1.0% w/v SLS is similar to its solubility in biorelevant media.
目標為速釋產(chǎn)品,因此預期在胃內(nèi)的溶出和在小腸上部內(nèi)的吸收���,建議使用具有低 pH 值的溶出介質(zhì)�。該產(chǎn)品的開發(fā)以 FDA 推薦的質(zhì)量控制溶出方法開始:900 mL0.1 N HCl 和 2.0% w/v SLS的溶出介質(zhì)����,用USP裝置2,75 rpm轉(zhuǎn)速����。初始開發(fā)的處方(批次1~11)顯示出快速溶出(30 分鐘(min)內(nèi)溶出度不低于 NLT 90%)����,與 RLD 類似�。對于團隊來說���,選擇體內(nèi)行為與 RLD 類似的制劑成為一種挑戰(zhàn)。測定了 acetriptan 在各種介質(zhì)中的溶解度(表 6)���,顯示 acetriptan 在 0.1 N HCl 和 1.0% w/v SLS 的介質(zhì)中的溶解度與其在生物相關(guān)性介質(zhì)中的溶解度類似���。
The dissolution method selected for product development uses 900 mL of 0.1 N HCl with 1.0% w/v SLS in a dissolution apparatus equipped with paddles (speed 75 rpm) and maintained at a temperature of 37°C, followed by UV spectroscopy at a wavelength of 282 nm. Dissolution in 1.0% w/v SLS is not sensitive to medium pH (similar in 0.1 N HCl, pH 4.5 buffer and pH 6.8 buffer) (data not shown). Additionally, this method is capable of detecting dissolution changes in the drug product caused by deliberately varying the drug substance (DS) particle size distribution (PSD) (see Section 1.4.2).
產(chǎn)品開發(fā)選擇的溶出方法使用了900 mL0.1 N HCl和1.0% w/v SLS的裝備槳(轉(zhuǎn)速75 rpm)的 溶出裝置,溫度維持在37°C����,然后是波長為282 nm的UV分光光度儀�。在1.0% w/v SLS中的溶出對介質(zhì)pH值(類似于在0.1 N HCl, pH 4.5緩沖液和pH 6.8緩沖液中)不敏感(數(shù)據(jù)未顯示)�。 此外����,該方法能檢測出通過故意改變藥物(DS)粒度分布(PSD)而引起的藥品的溶出變化(見 1.4.2節(jié))���。
1.4.2 Pilot Bioequivalence Study 中試生物等效性研究
Note to Reader: For low solubility drugs, pilot bioequivalence (BE) studies are invaluable to demonstrate that the in vitro dissolution used is appropriate. When pilot bioequivalence studies are conducted, the following is an example of how they should be described in the development report to support controls on critical attributes such as particle size and to understand the relationship between in vitro dissolution and in vivo performance. Inclusion of formulations that perform differently will help to determine if there is a useful in vivo in vitro relationship.
致讀者:對于低溶解度藥物,證明使用的體外溶出是適宜的中試生物等效性(BE)研究是極其 寶貴的�。當進行中試生物等效性研究時,以下為示范說明它們應怎樣在開發(fā)報告中描述以支 持對關(guān)鍵屬性如粒徑的控制和理解體外溶出和體內(nèi)性能間的相關(guān)性�。包括不同行為的處方將 有助于判斷是否對體內(nèi)外相關(guān)性有用�。
The formulation development studies identified drug substance particle size distribution as the most significant factor that impacts drug product dissolution (see Section 2.2.1.4). In order to understand the potential clinical relevance of drug substance particle size distribution on in vivo performance, a pilot bioequivalence (BE) study (Study # 1001) was performed in 6 healthy subjects (four-way crossover: three prototypes and the RLD at a dose of 20 mg).
處方開發(fā)研究確定藥物粒度分布是影響藥品溶出的最重要因素(見2.2.1.4節(jié))����。為理解因為粒度分布對體內(nèi)性能的潛在臨床意義�,在6個健康受試者內(nèi)進行了一項中試生物等效性(BE)研 究(Study # 1001) (四交叉:劑量為20 mg 的3個原型和1個RLD)�。
The formulation used to produce the three prototypes and the composition is shown in Table 7. The only difference between each prototype was the drug substance particle size distribution. Drug substance Lot #2, #3 and #4 with a d90 of 20 μm, 30 μm and 45 μm was used for prototype Batch 18, 19, and 20, respectively. Characterization of the drug substance lots is provided in Section 2.2.1.2, Table 19.
處方用于生產(chǎn) 3 個原型���,組分如表 7 所示�。各個原型間的唯一差異是藥物粒度分布����。用于原 型批 18����,19 和 20 的藥物批分別是#2,#3 和#4���,d90 分別是 20 μm����,30 μm 和 45 μm。藥物 批的特征見 2.2.1.2 節(jié),表 19�。
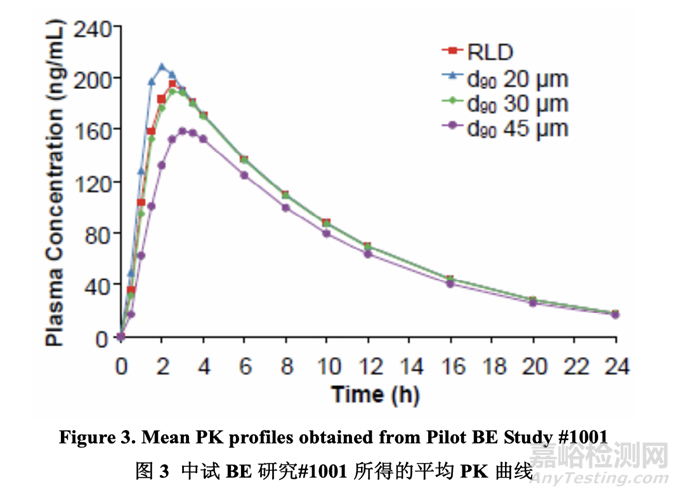
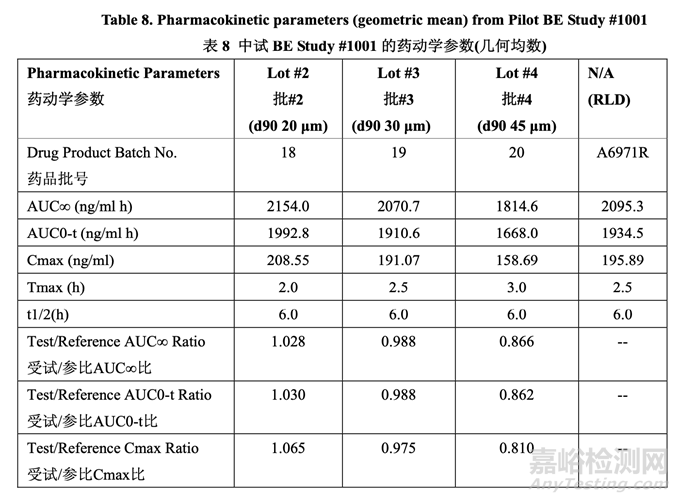 According to the literature3, when the mean Cmax and AUC responses of 2 drug products differ by more than 12-13%, they are unlikely to meet the bioequivalence limits of 80-125%. Therefore, the predefined selection criterion was a mean particle size that yielded both a Cmax ratio and an AUC ratio for test to reference between 0.9 and 1.11. The results of the PK study indicated that a drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 30 μm or less showed similar in vivo performance based on test to reference ratio calculations for AUC and Cmax. A drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 45 μm did not meet the predefined criterion of a test to reference ratio for Cmax and AUC between 0.9 and 1.11. The results confirmed the in silico simulation data obtained during preformulation work (see Section 2.2.1.2).
According to the literature3, when the mean Cmax and AUC responses of 2 drug products differ by more than 12-13%, they are unlikely to meet the bioequivalence limits of 80-125%. Therefore, the predefined selection criterion was a mean particle size that yielded both a Cmax ratio and an AUC ratio for test to reference between 0.9 and 1.11. The results of the PK study indicated that a drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 30 μm or less showed similar in vivo performance based on test to reference ratio calculations for AUC and Cmax. A drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 45 μm did not meet the predefined criterion of a test to reference ratio for Cmax and AUC between 0.9 and 1.11. The results confirmed the in silico simulation data obtained during preformulation work (see Section 2.2.1.2).
根據(jù)文獻���,當2種藥品的平均Cmax和AUC響應相差在12~13%以上時����,它們不可能符合生物等效性限度80~125%。因此���,預定義的選擇標準是平均粒徑����,可產(chǎn)生受試與參比的Cmax 比和AUC比介于0.9~1.1之間�。PK研究的結(jié)果表明藥物粒度分布的d90為30 μm或以下顯示出 類似的體內(nèi)性能���,基于計算的受試與參比的AUC比和Cmax比。藥物粒度分布的d90為45 μm 不符合受試與參比的Cmax比和AUC比介于0.9~1.1之間的預定義標準����。結(jié)果確認了在預處方 工作中得到的計算機模擬數(shù)據(jù)(見2.2.1.2節(jié))����。
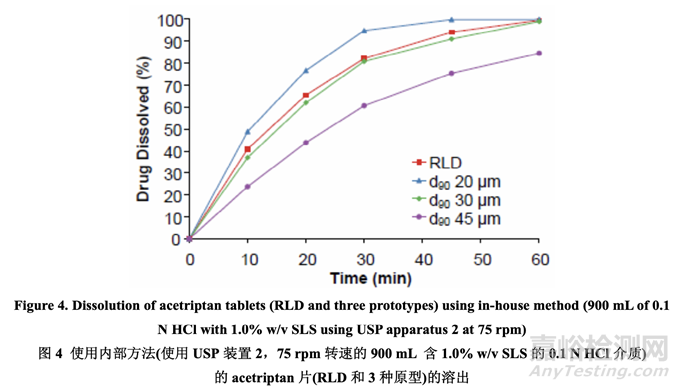
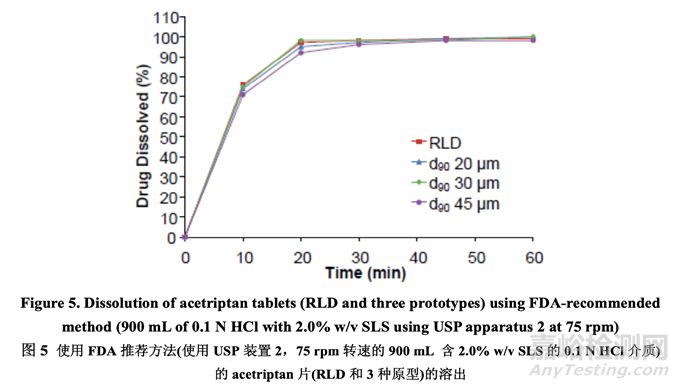
In order to understand the relationship between in vitro dissolution and in vivo performance, the dissolution test was performed on the three prototypes and the RLD using the in-house versus the FDA-recommended dissolution method. The results are presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively. The data indicated that the in-house dissolution method (with 1.0% w/v SLS) is capable of differentiating formulations manufactured using different drug substance particle size distributions. However, the FDA-recommended dissolution method (with 2.0% w/v SLS) is not sensitive to deliberate formulation changes in the drug substance particle size distribution for this BCS class II compound.
為理解體外溶出和體內(nèi)性能間的相關(guān)性����,使用內(nèi)部和 FDA-推薦的溶出方法���,對 3 個原型和 1 個 RLD 進行了溶出檢查�。結(jié)果分別見圖 4 和圖 5。數(shù)據(jù)表明內(nèi)部溶出方法(含 1.0% w/v SLS) 對該 BCS II 類化合物的藥物粒度分布中的處方故意變更不敏感����。
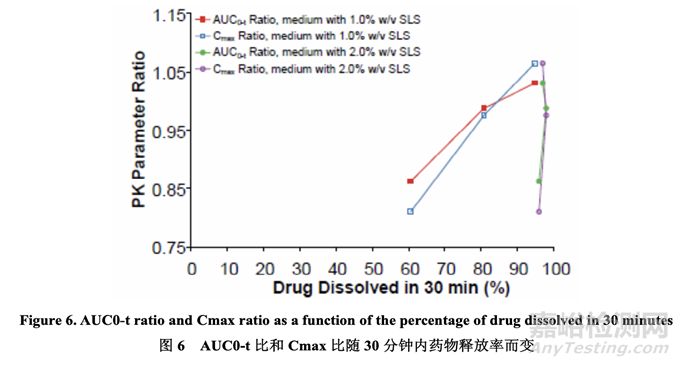
The AUC0-t ratio and Cmax ratio between the prototypes and the RLD were plotted versus the percentage of drug dissolved using both the in-house and FDA-recommended dissolution methods. The results are presented in Figure 6 and suggest that dissolution testing in medium with 1.0% w/v SLS and a 30 minute endpoint is predictive of the in vivo performance. However, the dissolution testing in medium with 2.0% w/v SLS was not able to predict the in vivo performance differences due to the drug substance particle size changes.
原型和 RLD 間的 AUC0-t 比和 Cmax 比對使用內(nèi)部和 FDA 推薦的溶出方法的藥物溶出率繪圖���。結(jié)果見圖 6����,表明在含 1.0% w/v SLS 的介質(zhì)中的溶出檢查和 30 分鐘終點可預測體內(nèi)性能���。但是���,在含2.0% w/v SLS的介質(zhì)中的溶出檢查不能預測體內(nèi)性能差異由于藥物粒徑變化���。
A dissolution rate of not less than (NLT) 80% in 30 minutes in 0.1 N HCl with 1.0% w/v SLS was set as the target for pharmaceutical development studies based on the fact that Batch 19 (d90 30μm) showed 80.8% dissolution in 30 minutes and demonstrated comparable pharmacokinetic profiles to the RLD in the pilot BE study.
設定在含 1.0% w/v SLS 的 0.1 N HCl 中,30 分鐘內(nèi)溶出率不低于(NLT) 80%為藥物開發(fā)研究 的目標是基于這樣的事實���,批 19 (d90 30 μm) 顯示在 30 分鐘內(nèi)溶出率為 80.8%并證明在中 試 BE 研究中藥動學曲線與 RLD 類似。
參考文獻:
Example QbD IR Tablet Module 3 Quality 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development���,F(xiàn)DA����,2012.



 According to the literature3, when the mean Cmax and AUC responses of 2 drug products differ by more than 12-13%, they are unlikely to meet the bioequivalence limits of 80-125%. Therefore, the predefined selection criterion was a mean particle size that yielded both a Cmax ratio and an AUC ratio for test to reference between 0.9 and 1.11. The results of the PK study indicated that a drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 30 μm or less showed similar in vivo performance based on test to reference ratio calculations for AUC and Cmax. A drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 45 μm did not meet the predefined criterion of a test to reference ratio for Cmax and AUC between 0.9 and 1.11. The results confirmed the in silico simulation data obtained during preformulation work (see Section 2.2.1.2).
According to the literature3, when the mean Cmax and AUC responses of 2 drug products differ by more than 12-13%, they are unlikely to meet the bioequivalence limits of 80-125%. Therefore, the predefined selection criterion was a mean particle size that yielded both a Cmax ratio and an AUC ratio for test to reference between 0.9 and 1.11. The results of the PK study indicated that a drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 30 μm or less showed similar in vivo performance based on test to reference ratio calculations for AUC and Cmax. A drug substance particle size distribution with a d90 of 45 μm did not meet the predefined criterion of a test to reference ratio for Cmax and AUC between 0.9 and 1.11. The results confirmed the in silico simulation data obtained during preformulation work (see Section 2.2.1.2).