This is an example pharmaceutical development report illustrating how ANDA applicants can move toward implementation of Quality by Design (QbD). The purpose of the example is to illustrate the types of pharmaceutical development studies ANDA applicants may use as they implement QbD in their generic product development and to promote discussion on how OGD would use this information in review.
FDA官網(wǎng)中一個(gè)有關(guān)藥物開發(fā)報(bào)告的實(shí)例�����,用以說明申請人如何實(shí)施質(zhì)量源于設(shè)計(jì)(QbD)����。 該實(shí)例的目的是說明ANDA申請人在其仿制藥開發(fā)過程中實(shí)施QbD時(shí),可使用的藥物開發(fā)研究的類型����,同時(shí)促進(jìn)探討OGD在審評中如何使用該信息。
本文主要概述了制劑開發(fā)中原料藥和輔料的關(guān)鍵要點(diǎn)。
2.1 Components of Drug Product 制劑組分
2.1.1 Drug Substance 原料藥
2.1.1.1 Physical Properties 物理性質(zhì) Physical description: 物理性狀:
The following physical description is for acetriptan Form III. 如下物理性狀適用于acetriptan III型�����。
Appearance: White to off-white, crystalline powder
外觀:白色至類白色�����,結(jié)晶性粉末
Particle morphology: Plate-like crystals
粒子形態(tài):板狀晶體
Particle size distribution: PSD of drug substance Lot #2 was measured using Malvern Mastersizer. The results were as follows: d10 – 7.2 μm; d50 – 12 μm; d90 – 20 μm. This is representative of the drug substance PSD selected for the final drug product formulation.
粒度分布:使用Malvern Mastersizer粒度儀測量原料藥批#2的PSD����。結(jié)果如下:d10– 7.2 μm; d50 – 12 μm; d90 – 20 μm。這可代表選擇用于最終藥品處方的原料藥 PSD����。
Solid state form: 固態(tài)形式:
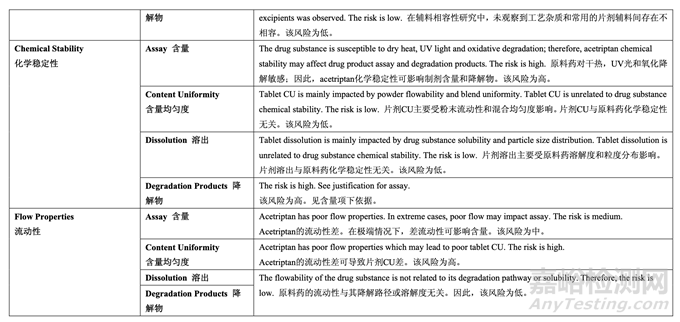
To date, three different crystalline forms (Form I, II and III) have been identified and reported in the literature. The three different forms were prepared using different solvents and crystallization conditions. The solubility and the melting point are different for each of the three polymorphs. Polymorphic Form III is the most stable form and has the highest melting point. The DMF holder provides acetriptan polymorphic Form III consistently based on in-house batch analysis data obtained by XRPD and DSC. Stress testing confirmed that no polymorphic conversion was observed (Table 10) and Form III is stable under the stress conditions of high temperatures, high humidity, UV light and mechanical stress. Since it is the most stable form, no phase transformation during the manufacturing process is expected. The Form III melting point and characteristic 2θ values are included in the drug substance specification as a part of the control strategy.
目前為止,已確定了3種不同晶型(I, II和III型)并報(bào)告在文獻(xiàn)中��。使用不同溶劑和結(jié)晶條件制備了3種不同晶型�����。3種多晶型物的每種溶解度和熔點(diǎn)都不相同����。
多晶型III最穩(wěn)定,熔點(diǎn)最高。 DMF持有人提供了穩(wěn)定的acetriptan多晶型III����,基于通過XRPD和DSC得到的內(nèi)部批分析數(shù)據(jù)。強(qiáng)降解測試確認(rèn)未觀察到多晶型轉(zhuǎn)換(表10)����,晶型III穩(wěn)定在高溫��,高濕��,UV光和機(jī)械 應(yīng)力的強(qiáng)降解條件下保持穩(wěn)定�����。因?yàn)檫@是最穩(wěn)定的晶型��,所以預(yù)期在生產(chǎn)工藝中無相變��。晶型III的熔點(diǎn)和2θ值的特征包括在原料藥質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)中作為控制策略的一部分����。
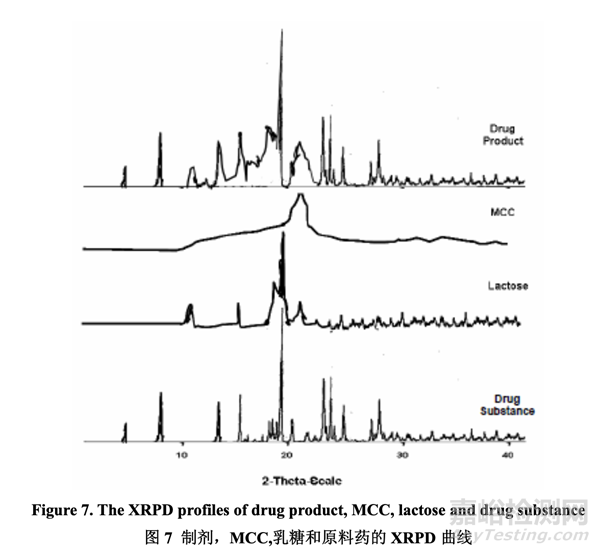
To confirm its physical stability, the final drug product was sampled during lab scale studies to evaluate whether processing conditions affected the polymorphic form of the drug substance. The XRPD data showed that the characteristics 2θ peaks of Form III of the drug substance are retained in the final drug product. Representative profiles are shown in Figure 7. An advanced XRPD technique was utilized to detect the possible phase transition in the drug product since the level of drug substance was 10% in the drug product.
為確認(rèn)其物理穩(wěn)定,在實(shí)驗(yàn)室規(guī)模研究中對最終藥品取樣以評估加工條件是否影響原料藥的 多晶型��。XRPD 數(shù)據(jù)表明原料藥晶型 III 的 2θ 峰特征在最終藥品中保持不變。代表性曲線見 圖 7��。使用一種先進(jìn)的 XRPD 技術(shù)來檢測藥品中可能的相變����,因?yàn)樗幤分性纤幍臐舛葹?10%。
The most stable polymorph (Form III) exhibits plate-like morphology as shown in Figure 8.
最穩(wěn)定的多晶型(III 型)顯示板狀形態(tài)�����,如圖 8 所示�����。
Melting point: Approximately 186 °C (Form III)
熔點(diǎn):約186 °C (III型)
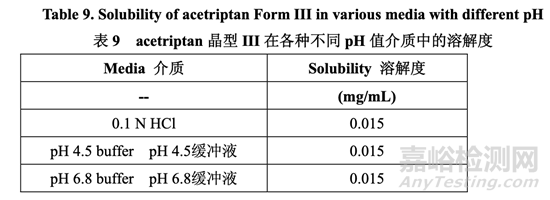
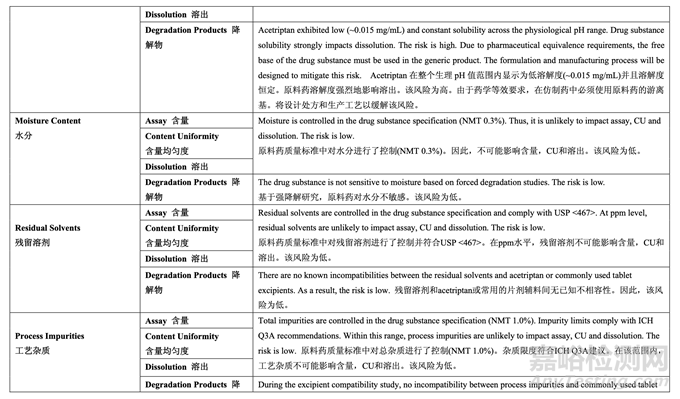
Aqueous solubility as a function of pH: 隨pH值而變的水性溶解度:The solubility of acetriptan Form III in aqueous media as a function of pH was measured and is presented in Table 9. The aqueous solubility of acetriptan is low (~0.015 mg/mL) and constant across the physiological pH range due to the lipophilic nature of the molecule.
測量了 acetriptan 晶型 III 在水性介質(zhì)中隨 pH 值而變的溶解度�����,見表 9����。Acetriptan 的水性溶 解度低(~0.015 mg/mL),在整個(gè)生理 pH 值范圍內(nèi)恒定��,由于分子的親脂性����。
Hygroscopicity: 吸濕性:
Acetriptan Form III is non-hygroscopic and requires no special protection from humidity during handling, shipping or storage. Hygroscopicity studies were carried out using a vapor sorption analyzer. The temperature was maintained at 25 °C. The material was exposed to stepwise increases in relative humidity from 10% to 90% for up to 150 minutes at each condition. The drug substance was non-hygroscopic, adsorbing less than 0.2% w/w at 90% RH.
Acetriptan晶型III為非吸濕�����,在處理��,運(yùn)輸或貯存中不需要專門避濕�����。使用蒸汽吸附分析儀 進(jìn)行了吸濕性研究。溫度維持在25 °C�����。每種條件下�����,物料暴露于逐步增加的相對濕度(10%~ 90%)下達(dá)150分鐘��。原料藥為非吸濕����,在90% RH下吸附量低于0.2% w/w��。
Density (Bulk, Tapped, and True) and Flowability: 密度(松密度��,振實(shí)密度和真密度)和流動性:The bulk, tapped and true density as well as the flowability of acetriptan Form III (Lot #2 : d10 – 7.2 μm; d50 – 12 μm; d90 – 20 μm) were measured.
測量了acetriptan晶型III (批#2 : d10 – 7.2 μm; d50 – 12 μm; d90 – 20 μm)的松密度��,振實(shí)密度 和真密度及流動性����。
Bulk density: 0.27 g/cc Tapped density: 0.39 g/cc True density: 0.55 g/cc
松密度:0.27 g/cc 振實(shí)密度:0.39 g/cc
真密度:0.55 g/cc
The flow function coefficient (ffc) was 2.95 and the Hausner ratio was 1.44 which both indicate
poor flow properties. The cohesiveness of the drug substance was also studied using a powder rheometer. The specific energy (12 mJ/g) of the drug substance indicates that the drug substance is cohesive.
流動系數(shù)(ffc)為 2.95 和 Hausner 比為 1.44 都表明流動相差����。同時(shí)使用粉末流動性測試儀研 究了原料藥的內(nèi)聚強(qiáng)度。原料藥的比能(12 mJ/g)表明原料藥具有粘性��。
2.1.1.2 Chemical Properties 化學(xué)性質(zhì)
pKa: Acetriptan is a weak base with a pKa of 9.2.
pKa: Acetriptan為弱堿�����,pKa值為9.2�����。
Chemical stability in solid state and in solution: 固態(tài)和溶液中的化學(xué)穩(wěn)定性:
Stress testing (forced degradation) was carried out on acetriptan to study its impurity profile, degradation pathway and to facilitate the development of a stability-indicating method. In addition, knowledge obtained from the forced degradation studies was used during formulation and process design and development to prevent impurities from being generated. The specified stress conditions were intended to achieve approximately 5-20% degradation (if possible) of acetriptan or to represent a typical stress condition even though less than 5% degradation was achieved due to its inherent stability. The stressed samples were compared to the unstressed sample (control). Stress conditions and results are listed in Table 10 below.
對 acetriptan 進(jìn)行了強(qiáng)降解測試以研究其雜質(zhì)概況��,降解路徑并有助于開發(fā)一種指示穩(wěn)定性 的方法��。此外,從強(qiáng)降解研究中得到的知識在處方和工藝設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)中用于防止雜質(zhì)產(chǎn)生��。 規(guī)定的強(qiáng)降解條件目的是實(shí)現(xiàn)約 5~20%acetriptan 降解(如可能)或表示一種典型的強(qiáng)降解條件即使實(shí)現(xiàn)了不到 5%降解由于其內(nèi)在穩(wěn)定性�����。強(qiáng)降解樣品與未強(qiáng)降解樣品(對照)進(jìn)行比較����。 強(qiáng)降解條件和結(jié)果列于以下表 10 中。
Samples were analyzed by HPLC equipped with a peak purity analyzer (photodiode array). Degradation peaks were well resolved from the main peak (acetriptan). The peak purity of the main peak and monitored degradants RC2 (ACE12345), RC3 (RRT = 0.68) and RC4 (RRT=0.79) were greater than 0.99. For each degradant, the peak purity angle was less than the peak purity threshold, suggesting that there was no interference of degradants with the main peak. Degradant RC1 was not observed. Degradant RC2 was formed due to oxidation and degradant RC3 was the result of further oxidation. Based on the results of the forced degradation studies, RC2 and RC3 were identified as the principal degradation products under the stress conditions. RC3 was not found under long-term stability conditions. With prolonged exposure to excessive high temperature (105 oC, 96 hours), 14% of RC4 was observed.
通過裝備峰純度分析儀(光電二極管陣列)的HPLC分析樣品����。降解峰與主峰(acetriptan)分離良 好����。主峰和監(jiān)測降解物RC2 (ACE12345), RC3 (RRT = 0.68)及RC4 (RRT=0.79)的峰純度都大 于0.99。對于每種降解物����,峰純度角低于峰純度閾值,表明降解物對主峰不產(chǎn)生干擾��。未觀 察到降解物RC1��。形成降解物RC2由于氧化作用,降解物RC3是進(jìn)一步氧化作用的結(jié)果��?�;趶?qiáng)降解研究的結(jié)果�����,確定RC2和RC3為強(qiáng)降解條件下的主要降解物����。長期穩(wěn)定性條件下未發(fā)現(xiàn)RC3。長時(shí)間暴露于過高溫度下(105 oC, 96小時(shí))��,觀察到14%的RC4����。
Overall, acetriptan is susceptible to dry heat, UV light and oxidative degradation. 總之,acetriptan 對干熱�����,UV 光和氧化降解敏感��。
2.1.1.3 Biological Properties 生物學(xué)性質(zhì)
Partition coefficient: Log P 3.55 (25 °C, pH 6.8) 分配系數(shù):Log P 3.55 (25 °C, pH 6.8) Caco-2 permeability: 34 × 10-6 cm/s Caco-2 滲透性:34 × 10-6 cm/s
The Caco-2 permeability is higher than the reference standard, metoprolol, which has a Caco-2 permeability of 20 × 10-6 cm/s. Therefore, acetriptan is highly permeable. Caco-2滲透性高于對照品����,美托洛爾��,其Caco-2滲透性為20 × 10-6 cm/s��。因此����,acetriptan為 高滲透性����。
Biopharmaceutics Classification: 生物藥劑學(xué)分類:
Literature and in-house experimental data support the categorization of acetriptan as a highly permeable drug substance. Based on its solubility across physiological pH (Table 9) acetriptan is designated as a low solubility drug substance. The calculated dose solubility volume is as follows: 文獻(xiàn)和內(nèi)部實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)支持acetriptan歸為高滲透性藥物?����;谄湓谡麄€(gè)生理pH內(nèi)的溶解度(表 9)��,指定acetriptan為低溶解度藥物�����。計(jì)算的劑量溶解度體積如下:
20 mg (highest strength)/(0.015 mg/mL) = 1333 mL > 250 mL
20 mg (最高規(guī)格)/(0.015 mg/mL) = 1333 mL > 250 mL
Therefore, acetriptan is considered a BCS Class II compound (low solubility and high permeability) according to the BCS guidance.
因此����,根據(jù)BCS指南�����,acetriptan被視為BCS II類化合物(低溶解度和高滲透性)��。2.1.1.4 Risk Assessment of Drug Substance Attributes 原料藥屬性的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評估
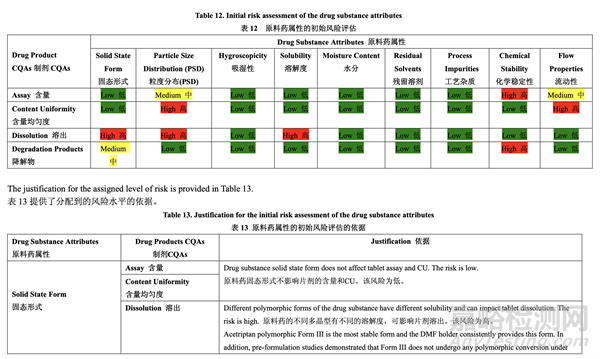
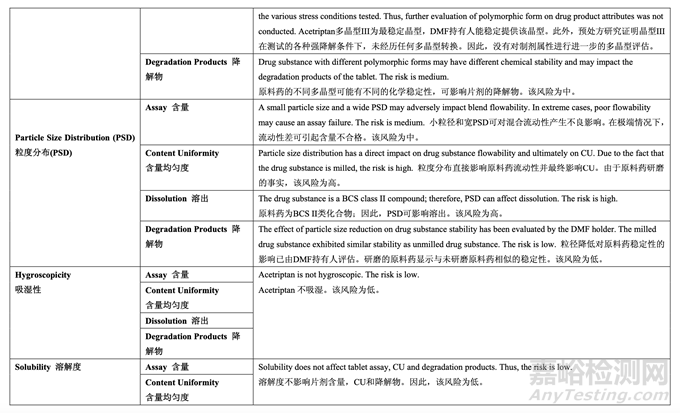
A risk assessment of the drug substance attributes was performed to evaluate the impact that each attribute could have on the drug product CQAs. The outcome of the assessment and the accompanying justification is provided as a summary in the pharmaceutical development report. The relative risk that each attribute presents was ranked as high, medium or low. The high risk attributes warranted further investigation whereas the low risk attributes required no further investigation. The medium risk is considered acceptable based on current knowledge. Further investigation for medium risk may be needed in order to reduce the risk. The same relative risk ranking system was used throughout pharmaceutical development and is summarized in Table 11. For each risk assessment performed, the rationale for the risk assessment tool selection and the details of the risk identification, analysis and evaluation are available to the FDA Reviewer upon request.
進(jìn)行原料藥屬性的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評估以評估每種屬性可能對制劑 CQAs 的影響��。評估結(jié)果和伴隨的依 據(jù)以總結(jié)方式提供于藥物開發(fā)報(bào)告中����。每個(gè)屬性顯示的相對風(fēng)險(xiǎn)以高��,中或低排列��。高風(fēng)險(xiǎn)屬性需進(jìn)一步的研究����,而低風(fēng)險(xiǎn)屬性無需進(jìn)一步的研究�����?���;诂F(xiàn)在的知識�����,中風(fēng)險(xiǎn)視為可接 受��?����?赡苄枰M(jìn)一步研究中風(fēng)險(xiǎn)以便降低風(fēng)險(xiǎn)�����。整個(gè)藥物開發(fā)中使用相同的相對風(fēng)險(xiǎn)排序系 統(tǒng)����,并總結(jié)在表 11 中。對于進(jìn)行的每個(gè)風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評估����,選擇風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評估工具的理由和詳細(xì)鑒別, 分析和評估風(fēng)險(xiǎn)見 FDA 基于要求的審查��。

Note to Reader: According to ICH Q9 Quality Risk Management, it is important to note that “it is neither always appropriate nor always necessary to use a formal risk management process (using recognized tools and/or internal procedures e.g., standard operating procedures). The use of informal risk management processes (using empirical tools and/or internal procedures) can also be considered acceptable. Appropriate use of quality risk management can facilitate but does not obviate industry’s obligation to comply with regulatory requirements and does not replace appropriate communications between industry and regulators.”4
致讀者:按照 ICH Q9 質(zhì)量風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理����,重要的是注意”使用正式的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理過程(使用認(rèn)可的 方法和/或內(nèi)部程序例如標(biāo)準(zhǔn)操作程序) 并非總是合適的或必要的。使用非正式的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理 過程(使用經(jīng)驗(yàn)方法和/或內(nèi)部程序) 也可被視為可接受����。質(zhì)量風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理的適當(dāng)使用可有助于 但不能排除遵守法規(guī)要求的行業(yè)義務(wù)�����,也不能取代行業(yè)和監(jiān)管機(jī)構(gòu)間的適宜溝通。“4
The two primary principles should be considered when implementing quality risk management:
實(shí)施質(zhì)量風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理時(shí)應(yīng)考慮兩個(gè)主要原則:
• The evaluation of the risk to quality should be based on scientific knowledge and ultimately link to the protection of the patient; and
質(zhì)量風(fēng)險(xiǎn)的評估應(yīng)基于科學(xué)知識并最終與保護(hù)患者相聯(lián)系;而且
• The level of effort, formality and documentation of the quality risk management process should be commensurate with the level of risk.
質(zhì)量風(fēng)險(xiǎn)管理過程中投入的努力程度��、管理的正式程度及文件管理水平應(yīng)與風(fēng)險(xiǎn)水平相適應(yīng)����。
Based upon the physicochemical and biological properties of the drug substance, the initial risk assessment of drug substance attributes on drug product CQAs is shown in Table 12. 基于原料藥的理化和生物學(xué)性質(zhì)����,原料藥屬性對制劑 CQAs 的初始風(fēng)險(xiǎn)評估見表 12。
2.1.2 Excipients 輔料
The excipients used in acetriptan tablets were selected based on the excipients used in the RLD, excipient compatibility studies and prior use in approved ANDA products that utilize roller compaction (RC). A summary of the excipient-drug substance compatibility studies and the selection of each excipient grade is provided in the following section.
選擇acetriptan片中使用的輔料是基于RLD中使用的輔料,輔料相容性研究和先用于已批準(zhǔn)的 使用碾壓(RC)的ANDA產(chǎn)品中�����。輔料-原料藥相容性研究和每種輔料級別的選擇總結(jié)見下節(jié)�����。
2.1.2.1 Excipient Compatibility Studies 輔料相容性研究
Note to Reader: Excipient compatibility is an important part of understanding the role of inactive ingredients in product quality. The selection of excipients for the compatibility study should be based on the mechanistic understanding of the drug substance and its impurities, excipients and their impurities, degradation pathway and potential processing conditions for the drug product manufacture. A scientifically sound approach should be used in constructing the compatibility studies. The commercial grades of the excipients are not provided in this example to avoid endorsement of specific products. However, in an actual pharmaceutical development report, the names of the commercial grades are expected.
輔料相容性是理解非活性成分在產(chǎn)品質(zhì)量中作用的重要部分。對于相容性研究的輔 料選擇應(yīng)基于理解原料藥和其雜質(zhì)��,輔料和其雜質(zhì)����,制劑生產(chǎn)的降解路徑和潛在加工條件的 機(jī)理����?�?茖W(xué)合理的方法應(yīng)用于構(gòu)造相容性研究中�����。該實(shí)例中不提供市售級的輔料以避免為某 些特定產(chǎn)品代言。但是��,在實(shí)際藥物開發(fā)報(bào)告中����,可預(yù)期市售級的名稱�����。
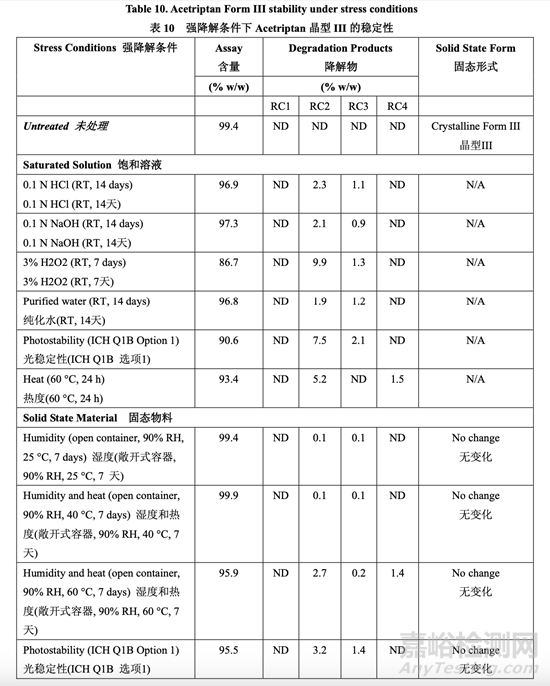
Excipient-drug substance compatibility was assessed through HPLC analysis of binary mixtures of excipient and drug substance at a 1:1 ratio in the solid state. Samples were stored at 25 °C/60 % RH and 40 °C/75 % RH in both open and closed containers for 1 month. Common excipients functioning as filler, disintegrant, and lubricant were evaluated in the excipient compatibility study. Table 14 summarizes the results.
通過 HPLC 分析固態(tài)下輔料與原料藥以 1:1 比例的二元混合物�����,來評估輔料-原料藥的相容 性。敞口容器和密封容器中的樣品貯存在 25 °C/60 % RH 和 40 °C/75 % RH 下各 1 個(gè)月��。輔 料相容性研究中評估作用為填充劑�����,崩解劑和潤滑劑的普通輔料�����。表 14 總結(jié)了結(jié)果。

Loss in assay or detection of degradants indicative of an incompatibility was not observed for the selected excipients except magnesium stearate. An interaction was seen with magnesium stearate at 40 °C/75 % RH. This interaction caused lower assay results for acetriptan. The mechanism for this interaction was indentified as formation of a magnesium stearate-acetriptan adduct (AD1) involving stearic acid. To further evaluate if this potential interaction could cause drug instability, an additional experiment was performed in which several different mixtures of drug and excipients were prepared. Only the excipient types used in the RLD formulation were selected for this study. The first mixture consisted of drug and all excipients in the ratio representative of the finished product. In subsequent mixtures, one excipient was removed at a time. These mixtures were stored at 25 °C/60% RH and 40 °C/75% RH in both open and closed containers for 1 month. Table 15 presents the results of the study.
對于所選的輔料除硬脂酸鎂外,未觀察到表示不相容性的含量損失或檢測到降解物����。在 40 °C/75 % RH 下,觀察到與硬脂酸鎂的相互作用。該相互作用引起 acetriptan 含量結(jié)果較低����。 該相互作用的機(jī)理確定為形成一種包括硬脂酸的硬脂酸鎂- acetriptan加合物(AD1)。為進(jìn)一 步評估該潛在相互作用是否可引起藥物不穩(wěn)定�,進(jìn)行了一額外實(shí)驗(yàn)���,制備了藥物和輔料的幾 種不同混合物����。該研究僅選擇 RLD 處方中使用的輔料類型�。第一種混合物包括代表成品比 例的藥物和所有輔料。在隨后的混合物中�,每次去掉一種輔料���。在 25 °C/60 % RH 和 40 °C/75 % RH 下�,這些混合物貯存在敞口容器和密封容器中各 1 個(gè)月����。研究的結(jié)果見表 15。
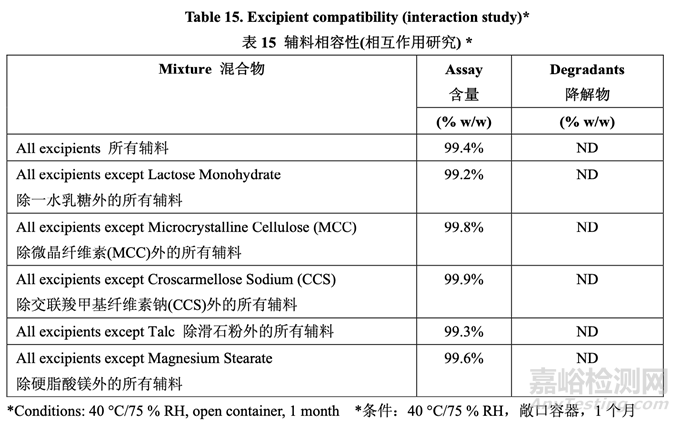
No loss in assay was observed in any of these mixtures at 40 °C/75% RH or at 25 °C/60% RH. There is no incompatibility with the selected excipients except for the noted interaction with magnesium stearate in the binary mixture study. Therefore, magnesium stearate was still selected, but contact of the drug substance with magnesium stearate was limited by only using extragranular magnesium stearate. Intragranular lubrication required for the roller compaction process was achieved by using talc. Subsequent assurance of compatibility was provided by long-term stability data for formulations used in the pilot BE study and the ongoing prototype stability studies using the formulation proposed for commercialization. The impurity method is able to identify and quantify AD1. Adduct formation was below the limit of quantitation in the long-term stability study and is controlled by the limit for any unspecified impurity.
在40 °C/75% RH 或25 °C/60%RH下�,在這些混合物中的任意一種未觀察到含量損失�。在二 元混合物研究中���,除注意到與硬脂酸鎂相互作用外,與所選輔料無不相容性����。因此���,仍然選 擇硬脂酸鎂,但是通過僅使用外加硬脂酸鎂來限制原料藥與硬脂酸鎂的接觸���。通過使用滑石 粉來實(shí)現(xiàn)碾壓所需的顆粒內(nèi)潤滑�。隨后通過提供用于中試BE研究的處方的長期穩(wěn)定性數(shù)據(jù) 和正在進(jìn)行的���,使用擬定用于工業(yè)化的處方的原型穩(wěn)定性研究來保證相容性。雜質(zhì)方法能鑒 定和定量AD1�。長期穩(wěn)定性研究中形成的加合物低于定量限,通過該限度來控制任何未指定雜質(zhì)���。
2.1.2.2 Excipient Grade Selection 輔料級別選擇
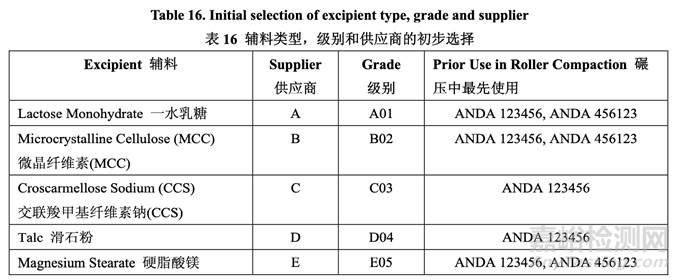
Based on the results of excipient compatibility studies, identical excipient types to the RLD formulation were selected for the generic product development. The selection of excipient grade and supplier was based on previous formulation experience and knowledge about excipients that have been used successfully in approved products manufactured by roller compaction as given in Table 16. The level of excipients used in the formulation were studied in subsequent formulation development studies.
基于輔料相容性研究的結(jié)果����,選擇與 RLD 處方相同的輔料類型用于仿制藥開發(fā)�。輔料級別 和供應(yīng)商的選擇是基于之前的處方經(jīng)驗(yàn)和關(guān)于已成功地用于已批準(zhǔn)的通過碾壓生產(chǎn)的藥品 中的輔料的知識�,如表 16 所示���。處方中使用的輔料濃度在隨后的處方開發(fā)研究中進(jìn)行研究。
Microcrystalline cellulose and lactose monohydrate comprise about 80% of the total drug product composition. Microcrystalline cellulose and lactose monohydrate are among the commonly used fillers for dry granulation formulations, both individually and in combination with each other, because they exhibit appropriate flow and compression properties. The particle size distribution, particle morphology, aspect ratio, bulk density and flowability of different grades have the potential to affect drug product content uniformity. Therefore, additional particle size controls above those in the pharmacopoeia are included in the specifications for the two major excipients: lactose monohydrate (d50: 70-100 μm) and microcrystalline cellulose (d50: 80-140 μm). Material within these ranges was used in all further formulation studies.
微晶纖維素和一水乳糖構(gòu)成約80%的總制劑組分���。微晶纖維素和一水乳糖是屬于普遍用于干 法制粒處方中使用的填充劑,可單獨(dú)使用及互相一起使用,因?yàn)樗鼈冿@示出適宜的流動性和 壓縮性。不同級別的粒度分布�,粒子形態(tài),縱橫比����,松密度和流動性可潛在影響制劑含量均 勻度。因此,對于兩種主要輔料����,除藥典規(guī)定外,質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)中包括了額外粒徑控制:一水乳 糖(d50:70~100 μm)和微晶纖維素(d50:80~140 μm)����。在所有進(jìn)一步的處方研究中使用在 這些范圍內(nèi)的物料���。
Lactose Monohydrate: Lactose monohydrate is commonly used as a filler. The potential impurities of lactose are melamine and aldehydes. The supplier has certified that the lactose is free of melamine and has provided a certificate of suitability for TSE/BSE. Lactose monohydrate Grade A01 from supplier A was selected based on successful product development in approved ANDA 123456 and ANDA 456123, both of which used roller compaction. The selected grade provides acceptable flow and compression properties when used in combination with microcrystalline cellulose.
一水乳糖:一水乳糖普遍作為填充劑使用。乳糖的潛在雜質(zhì)是三聚氰胺和醛����。供應(yīng)商證明該 乳糖不含三聚氰胺并提供了 TSE/BSE 的適用性證明�?;谠谝雅鷾?zhǔn)都使用碾壓的 ANDA 123456 和 ANDA 456123 中成功的產(chǎn)品開發(fā)�,選擇供應(yīng)商 A,級別 A01 的一水乳糖。所選 的級別提供了可接受的流動性和壓縮性當(dāng)與微晶纖維素聯(lián)合使用時(shí)。
Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC): Microcrystalline cellulose is widely used as a filler for direct compression and roller compaction. Though it is reported in the literature that MCC may
physically bind or adsorb drug substance, no such physical interaction was evident in the formulation dissolution studies. It is known from the literature that MCC undergoes plastic deformation during compaction since it is a fibrous material and ductile in nature. Not all grades of MCC may be suitable for use in roller compaction. Microcrystalline cellulose Grade B02 from supplier B was selected based on the acceptable flow and compression properties when used in combination with lactose monohydrate as demonstrated in approved ANDA 123456 and ANDA 456123.
微晶纖維素(MCC):微晶纖維素廣泛作為直壓和碾壓的填充劑使用����。雖然有文獻(xiàn)報(bào)告MCC 可實(shí)際粘合或吸附原料藥,但是在處方溶出研究中���,此類物理相互作用不顯著�。從文獻(xiàn)上可 知MCC在壓縮中經(jīng)歷了塑性變形因?yàn)樗抢w維材料���,本質(zhì)上具有可塑性�。不是所有級別的 MCC可適用于在碾壓中使用�。基于當(dāng)與一水乳糖聯(lián)合使用時(shí)的可接受流動性和壓縮性���,如 已批準(zhǔn)的ANDA 123456 和ANDA 456123所示���,選擇供應(yīng)商B�,級別B02的微晶纖維素���。
Croscarmellose Sodium (CCS): Acetriptan is a BCS class II drug so rapid disintegration is necessary to ensure maximum bioavailability. Being a superdisintegrant, croscarmellose sodium is hygroscopic in nature. It swells rapidly to about 4-8 times its original volume when it comes in contact with water. Grade C03 from supplier C was selected. 交聯(lián)羧甲基纖維素鈉(CCS):Acetriptan為BCS II類藥物���,因此需要快速崩解以保證生物利用 度最大化。作為一種超級崩解劑����,交聯(lián)羧甲基纖維素鈉本質(zhì)上具有吸濕性�。當(dāng)它接觸到水時(shí)����, 膨脹至其原體積的約4~8倍����。選擇供應(yīng)商C的級別C03。
Talc: Talc is a common metamorphic mineral and is used as a glidant and/or lubricant both intragranularly and extragranularly in the formulation. Intragranular talc was used to prevent sticking during the roller compaction process. Because of the interaction between magnesium stearate and acetriptan, talc was also added extragranularly to reduce the level of magnesium stearate needed for the lubrication. Grade D04 from supplier D was selected.
滑石粉:滑石粉是普通的變質(zhì)礦物�,在處方中作為內(nèi)加和外加助流劑和/或潤滑劑使用。內(nèi) 加滑石粉用于防止碾壓工藝中發(fā)生粘結(jié)。因?yàn)橛仓徭V和acetriptan間的相互作用���,也以外加 方式加入滑石粉以降低潤滑所需的硬脂酸鎂濃度�。選擇供應(yīng)商D的級別D04。
Magnesium Stearate: It is the most commonly used lubricant for tablets. Because magnesium stearate interacts with acetriptan to form an adduct, it is used only extragranularly. Magnesium stearate grade E05 from supplier E was selected and is of vegetable origin.
硬脂酸鎂:普遍作為片劑的潤滑劑使用。因?yàn)橛仓徭V和 acetriptan 間的相互作用可形成加 合物���,所以僅以外加方式使用。選擇供應(yīng)商 E�,級別 E05,來自植物源的硬脂酸鎂����。
參考文獻(xiàn):
Example QbD IR Tablet Module 3 Quality 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development���,F(xiàn)DA�,2012.