This is an example pharmaceutical development report illustrating how ANDA applicants can move toward implementation of Quality by Design (QbD). The purpose of the example is to illustrate the types of pharmaceutical development studies ANDA applicants may use as they implement QbD in their generic product development and to promote discussion on how OGD would use this information in review.
FDA官網(wǎng)中一個有關(guān)藥物開發(fā)報告的實例��,用以說明申請人如何實施質(zhì)量源于設(shè)計(QbD)����。 該實例的目的是說明ANDA申請人在其仿制藥開發(fā)過程中實施QbD時����,可使用的藥物開發(fā)研究的類型,同時促進探討OGD在審評中如何使用該信息�。
本文主要概述了制劑的生產(chǎn)工藝放大以及控制策略。
2.3.6 Scale-Up from Lab to Pilot Scale and Commercial Scale
從實驗室規(guī)模放大至中試規(guī)模和工業(yè)規(guī)模
Note to Reader: Currently, scale-up information is limited at the time of submission. The applicant should discuss product specific scale-up principles including their planned approach to scale-up the process. OGD will evaluate the applicant’s plan to determine its adequacy. However, if a substantial amendment needs to be submitted due to the inadequacy of the scale-up plan, it may significantly extend the review process. It is the firm’s discretion to submit scale-up data such as actual process verification information at the time of submission for a complex drug product which has a high risk of scale-up failure; however, in some cases it may be requested by OGD.
通常�,遞交時的放大信息是有限的。申請人應(yīng)討論產(chǎn)品具體放大原則包括它們計劃 放大工藝的方法��。OGD將評估申請人的計劃以決定其適宜性��。但是��,如果需要提交實質(zhì)性 修正由于放大計劃不適宜��,則可顯著延長審查過程�。對于公司可酌情遞交放大數(shù)據(jù)如遞交具 有放大失敗高風(fēng)險的復(fù)方藥品時的實際工藝驗證信息;但是,某些情況下��,OGD可能要求 遞交��。
Process development was conducted on the lab scale (5.0 kg). This section describes the principles used to scale-up the process to the pilot scale (50.0 kg) in order to manufacture the exhibit batch. The same principles will be employed to scale-up the process to the commercial scale uponapproval. Table 50 summarizes the different process scales.
進行了實驗室規(guī)模(5.0 kg)的工藝開發(fā)����。本節(jié)描述了用于放大至中試規(guī)模(50.0 kg)的工藝原則 以便生產(chǎn)申報批。一旦批準(zhǔn)��,將使用相同原則用于放大至工業(yè)規(guī)模的工藝原則����。表 50 總結(jié) 了半天的工藝規(guī)模。
2.3.6.1 Scale-Up of the Pre-Roller Compaction Blending and Lubrication Process
預(yù)碾壓混合和潤滑工藝的放大
The process development work for the pre-roller compaction blending and lubrication step was carried out in a 16 qt capacity twin shell V-blender. To scale-up, it was desirable to maintain geometric, dynamic and kinematic similarity by applying the following rules: 預(yù)碾壓混合和潤滑步驟的工藝開發(fā)工作在16 qt容量雙筒V型混合機內(nèi)進行��。為達到放大��,通 過使用如下規(guī)則來維持幾何相似����,動力相似和運動相似是可行的:
● Geometric similarity: keeping the ratio of all lengths constant (constant fill ratio) 幾何相似:所有長度比保持恒定(填充比恒定)
● Dynamic similarity: maintaining constant forces (Froude number Fr) 動力相似:維持恒力(Froude數(shù)Fr)
Fr= rpm2R/g
rpm: revolutions per minute 每分鐘轉(zhuǎn)數(shù) R:characteristic radius 特征半徑 g:gravitational constant 引力常數(shù)
● Kinematic similarity: maintaining a consistent number of revolutions (rpm × minutes) 運動相似:維持轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)穩(wěn)定(rpm ×分鐘)
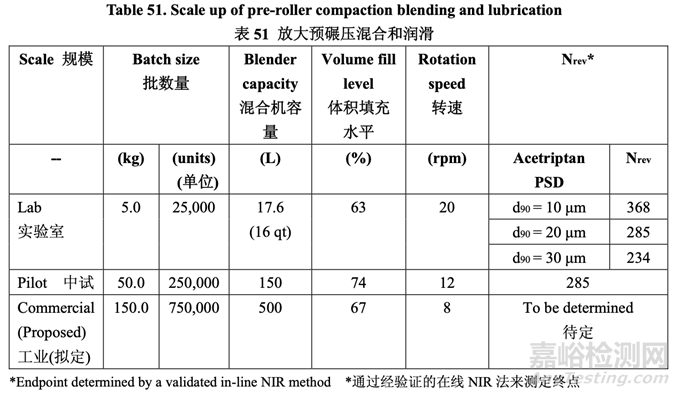
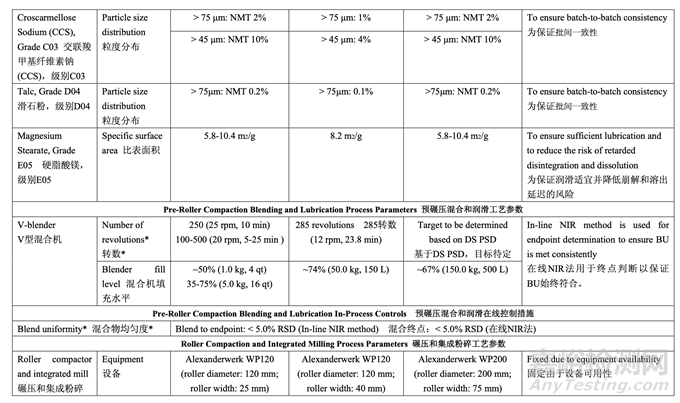
At the pilot scale, the fill level was 74%. This was slightly higher than the fill level at lab scale which was 63%. The rotation speed at both scales was fixed due to equipment constraints. Although the target blending endpoint could be estimated by maintaining similarity between the scales, the final endpoint was determined using the validated in-line NIR method (details provided in Section 3.2.P.5.3 Validation of Analytical Procedures). To assess homogeneity of the blend, a moving block % RSD was calculated for each moving block of ten consecutive spectra and plotted as a function of time. The blend was considered uniform once the % RSD was below 5% for ten consecutive measurements.
在中試規(guī)模����,填充水平為74%�。這稍微比實驗室填充水平(63%)高。由于設(shè)備限制����,固定了 兩個規(guī)模的轉(zhuǎn)速。雖然目標(biāo)混合終點可通過維持兩個規(guī)模間的相似性來估計�,但使用經(jīng)驗證 的在線NIR法(具體見3.2.P .5.3節(jié)分析方法驗證)來測定最終終點。為評估混合物的均勻性����,計 算10個連續(xù)光譜中每個移動區(qū)的移動區(qū)%RSD并根據(jù)時間繪圖。一旦10個連續(xù)測量值的 %RSD低于5%����,可認(rèn)為混合均勻。
The pre-roller compaction blending and lubrication process scale-up is summarized in Table 51.
表 51 總結(jié)了預(yù)碾壓混合和潤滑工藝的放大��。
2.3.6.2 Scale-Up of the Roller Compaction and Integrated Milling Process
碾壓和集成粉碎工藝的放大
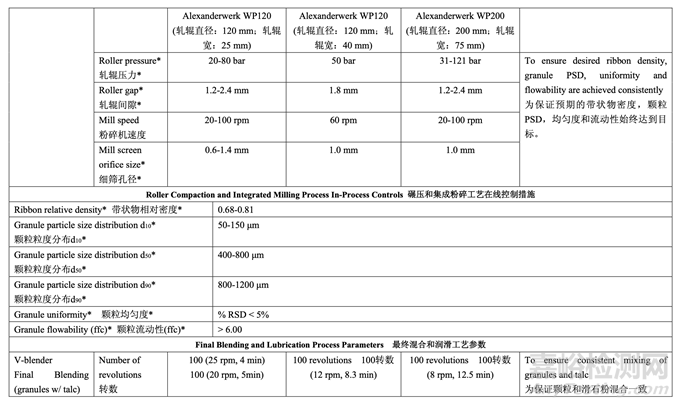
For this drug product, the roller compaction process first needed to be scaled up from lab scale (using Alexanderwerk WP120 with 120 mm roll diameter and 25 mm roll width) to pilot scale (using Alexanderwerk WP120 with 120 mm roll diameter and 40 mm roll width) and then, ultimately, to commercial scale (using Alexanderwerk WP200 with 200 mm roll diameter and 75 mm roll width).
對于該制劑�,碾壓工藝首先需要從實驗室規(guī)模(使用軋輥直徑為120 mm和軋輥寬為25 mm的 Alexanderwerk WP120)放大中試規(guī)模(使用軋輥直徑為120 mm和軋輥寬為40 mm的 Alexanderwerk WP120),并最終放大至工業(yè)規(guī)模(使用軋輥直徑為200 mm和軋輥寬為75 mm 的Alexanderwerk WP 200)��。
In a roller compaction process, there are several process parameters to consider when scaling up to a larger, wider roller. The strategy employed for each process parameter is discussed below. 碾壓工藝中,當(dāng)放大至較大����,較寬軋輥時����,需考慮幾個工藝參數(shù)。每個工藝參數(shù)使用的策略 討論如下����。
Roller Gap 軋輥間隙
The scale-up strategy for the roller gap was to maintain the ratio between the roller gap (S) and the roller diameter (D) for different size roller compactors. The scale-up factor for the roller gap was calculated according to the following equation: 軋輥間隙的放大策略是維持不同大小壓實機的軋輥間隙(S)和軋輥直徑(D)的比。按照如下方 程計算軋輥間隙的放大系數(shù):
S1/D1= S2/D2
Roll Force or Roll Pressure 軋輥力或軋輥壓力
Based on the process development work, ribbon density was an intermediate critical quality attribute for this process step and strongly affected the downstream compression force required to meet the target tablet hardness. A commonly used strategy to scale-up roller compaction is to control the ribbon density by maintaining the roller peak pressure (Pmax) as described by Johanson’s model.
基于工藝開發(fā)工作�,帶狀物密度是該工藝步驟的中間體關(guān)鍵質(zhì)量屬性,強烈地影響需符合片 劑目標(biāo)硬度的下游壓縮力��。放大碾壓的常用策略是通過維持軋輥峰壓力(Pmax)來控制帶狀物 密度����,如 Johanson 模型所示。
According to the model, if the S/D ratio is maintained, a scale-up strategy is to obtain the same Pmax by maintaining the Rf /(W×D) ratio where Rf is the roller force and W is the roller width. The scale-up factor for roller force is calculated by:
根據(jù)該模型��,如果維持 S/D 比�,則放大策略是通過維持 Rf /(W×D)比來得到相同的 Pmax, 此 處 Rf 為軋輥力����,W 為軋輥寬����。通過如下計算軋輥力的放大系數(shù):
Rf2/Rf1= W2D2/ W1D1
If roller hydraulic pressure is used, it is necessary to obtain the conversion factor between roller hydraulic pressure (bar) to roller force (kN) from the equipment vendor. 如果使用軋輥液壓�,則必須從設(shè)備供應(yīng)商得到軋輥液壓(bar)與軋輥力(kN)間的換算系數(shù)。 Alexanderwerk provided the following information:
Alexanderwerk提供了如下信息:
For WP120: 0.0922 kN per cm of roller width for 1 bar roller pressure WP120:軋輥寬0.0922 kN/cm對應(yīng)于1 bar軋輥壓力
For WP200: 0.0869 kN per cm of roller width for 1 bar roller pressure WP200:軋輥寬0.0869 kN/cm對應(yīng)于1 bar軋輥壓力
The scale-up factor for roller pressure was calculated by:
通過如下計算軋輥壓力的放大系數(shù):
Rp2/Rp1= 0.0869×D2/ 0.0922×D1
Screw Speed and Roll Speed 螺桿轉(zhuǎn)速和軋輥速度
Assuming no slip at the roller surface in the nip region (i.e., the material is moving at the same speed as the rollers), the mass flow rate (throughput, Q, g/min) of material can be calculated based on mass balance: 假設(shè)捏合區(qū)的軋輥表面無滑移(即物料以與軋輥相同的速度移動)����,基于質(zhì)量平衡可計算物料 的質(zhì)量流率(生產(chǎn)量,Q�,g/min):
Q=ρπDWSNR
where ρ is the ribbon density (g/cc), D is the roller diameter (cm), W is the roller width (cm), S is
the roller gap (cm) and NR is the roller rotation speed (rpm).
此處,ρ 為帶狀物密度(g/cc)��,D 為軋輥直徑(cm)��,W 為軋輥寬(cm)��,S 為軋輥間隙�,NR 為 軋輥轉(zhuǎn)速(rpm)。
The powder material is conveyed to the rollers by the screw auger and the mass flow rate is typically proportional to the screw rotation rate: 粉狀物料通過螺旋鉆頭輸送到軋輥�,質(zhì)量流率一般與螺桿轉(zhuǎn)速成正比:
Q= CS NS
where, NS is the feed screw rotation speed (rpm) and CS is the amount of material conveyed by
the screw per rotation (g/rotation) which can be determined experimentally.
此處,NS 為螺旋加料器轉(zhuǎn)速(rpm)�,CS 為每次旋轉(zhuǎn)通過螺桿輸送的物料量(g/旋轉(zhuǎn)),這可通 過實驗測定����。
To achieve the target ribbon density for the given roller gap, the ratio of screw speed to roller speed was maintained constant by setting the two equations for mass flow rate equal to each other as shown below: 為達到給定軋輥間隙的帶狀物目標(biāo)密度����,螺桿轉(zhuǎn)速與軋輥速度的比應(yīng)通過設(shè)置質(zhì)量流率彼此 相等的兩個方程來維持恒定����,如下所示:
NS/NR=ρπDWS/ CS
Mill Screen Orifice Size and Mill Speed 細(xì)篩孔徑和粉碎機速度
Mill screen orifice size is a scale-independent variable; therefore, it is kept constant upon scale-up. During development, mill speed was not found to be critical for any product quality attributes. In practice, mill speed is set based on first-in first-out principles to avoid ribbon accumulation in the mill. 細(xì)篩孔徑是與規(guī)模無關(guān)的變量;因此��,一旦放大后�,保持恒定。開發(fā)中�,發(fā)現(xiàn)粉碎機速度是 任何產(chǎn)品質(zhì)量屬性的關(guān)鍵。實際上����,基于先進先出原則,設(shè)置粉碎機速度以避免帶狀物積聚 在粉碎機中����。
Table 52 summarizes the roller compaction and integrated milling process scale-up.
表 52 總結(jié)了碾壓和集成粉碎工藝的放大。
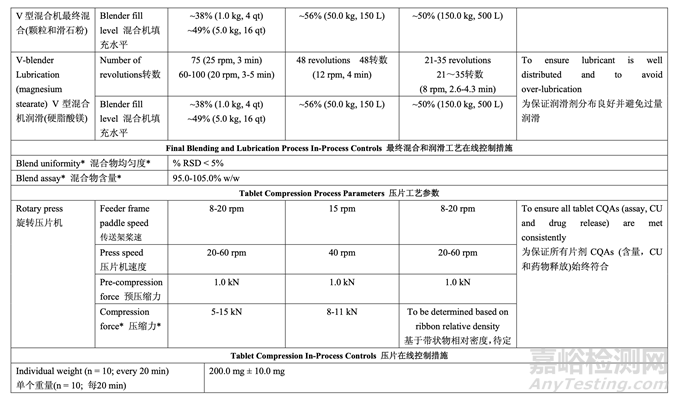
2.3.6.3 Scale-Up of the Final Blending and Lubrication Process
最終混合和潤滑工藝的放大
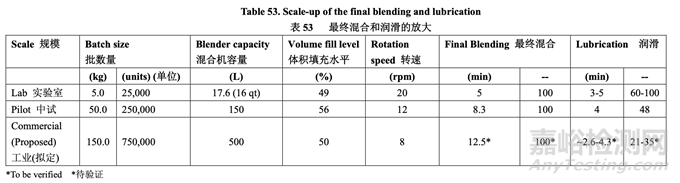
To scale-up the final blending of the granules with talc, the number of revolutions was maintained. 維持轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)以放大顆粒和滑石粉的最終混合����。
A different strategy was employed to scale-up the final lubrication. Recently, an equation for scaling up the lubrication of a 1:1 MCC:Lactose blend with magnesium stearate was published.16 If the batch size and blender volume of the new process are known, the number of revolutions to be used at the new process condition can be evaluated using the following equation:
不同的策略用于放大最終潤滑����。最近����,公布了一種可放大 1:1 MCC:乳糖的混合物和硬脂酸鎂潤滑的方程。16 如果已知批數(shù)量和新工藝的混合機容量����,則 使用如下方程可評估新工藝條件下使用的轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)
r2= (V1/3 Fheadspace r)1/(V1/3 Fheadspace r)2
where V is the blender volume, Fheadspace is the headspace fraction (calculated by 100% - fill level %), and r is the number of revolutions. The number of revolutions needed to lubricate the granules with magnesium stearate was calculated based on this equation. The final blending and lubrication process scale-up is summarized in Table 53.
此處,V 為混合機容量����,F(xiàn)headspace 為頂空部分(由 100%-填充水平%計算),r 為轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)�。基于該方程計算顆粒和硬脂酸鎂潤滑所需的轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)��。表 53 總結(jié)了最終 混合和潤滑工藝的放大����。
2.3.6.4 Scale-Up of the Tablet Compression Process 壓片工藝的放大
The same tablet press utilized during the tablet compression process development studies was used for the pilot batch and will be used for commercial scale production. Detailed parameters that affect the tabletting process were already explored and discussed in Section 2.3.5. To increase throughput, all 51 stations were used at the pilot scale successfully and will be used at the commercial scale. The press will be run at the same speed that was studied during development (20-60 rpm). Therefore, dwell time remains unchanged during scale-up.
在壓片工藝開發(fā)研究中使用的相同的壓片機用于中試批并將用于工業(yè)規(guī)模生產(chǎn)。2.3.5節(jié)已考察并討論了影響壓片工藝的詳細(xì)參數(shù)����。為增加生產(chǎn)量��,中試 規(guī)模下成功地使用了所有51個沖模數(shù)并將在工業(yè)規(guī)模下使用����。壓片機將以開發(fā)中研究的相同速度(20~60 rpm)運行����。因此,停頓時間在放大中保持不變����。
2.3.7 Exhibit Batch 申報批
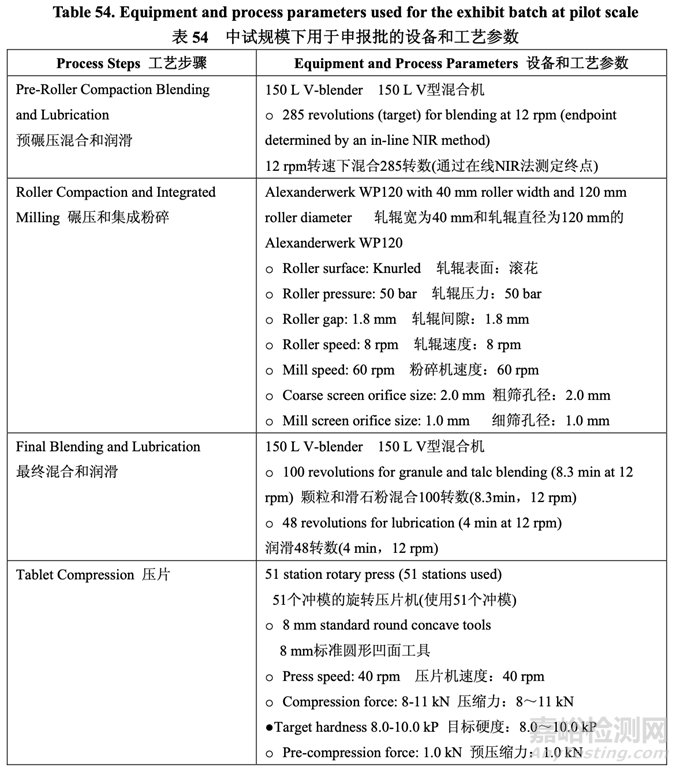
Based on the scale-up principles detailed in Section 2.3.6, a 50.0 kg cGMP exhibit batch was manufactured with drug substance Lot #2 at the pilot scale and the batch was used for the pivotal BE study. Table 54 summarizes the equipment and process parameters used for the exhibit batch at pilot scale.
基于 2.3.6 節(jié)中的具體放大原則�,在中試規(guī)模下使用原料藥批號 2 生產(chǎn)了一個 50.0 kg cGMP 的申報批,該批用于關(guān)鍵 BE 研究�。表 54 總結(jié)了中試規(guī)模下用于申報批的設(shè)備和工藝參數(shù)。
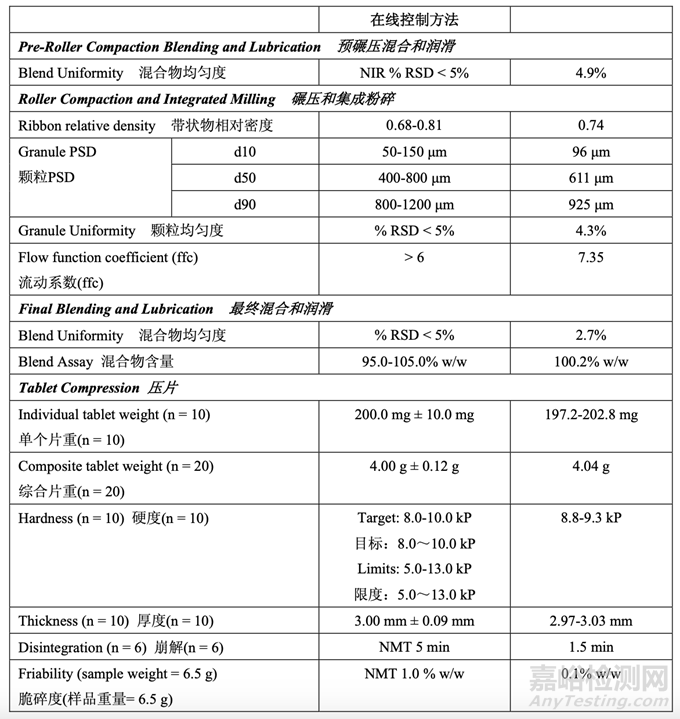
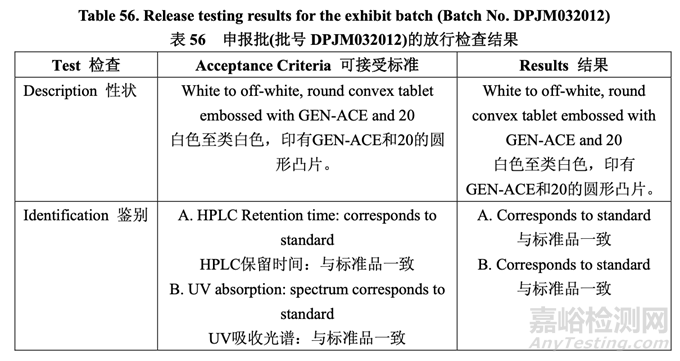
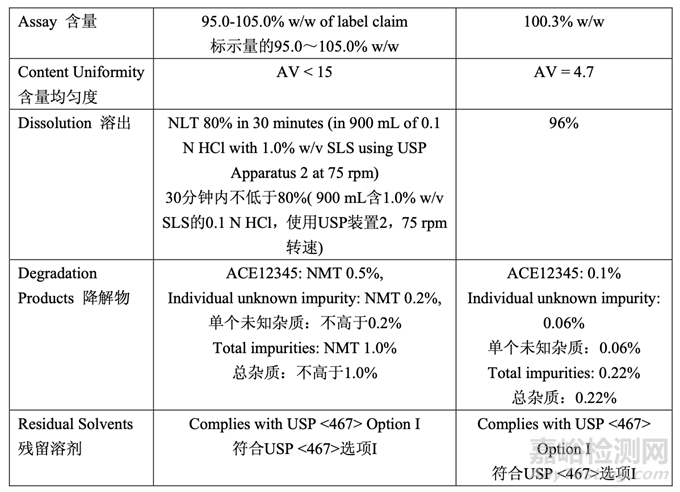
The in-process testing and final release results are summarized in Table 55 and Table 56, respectively.
表 55 和表 56 分別總結(jié)了在線檢查和最終放行結(jié)果�。
2.3.8 Updated Risk Assessment of the Drug Product Manufacturing Process
更新的制劑生產(chǎn)工藝的風(fēng)險評估
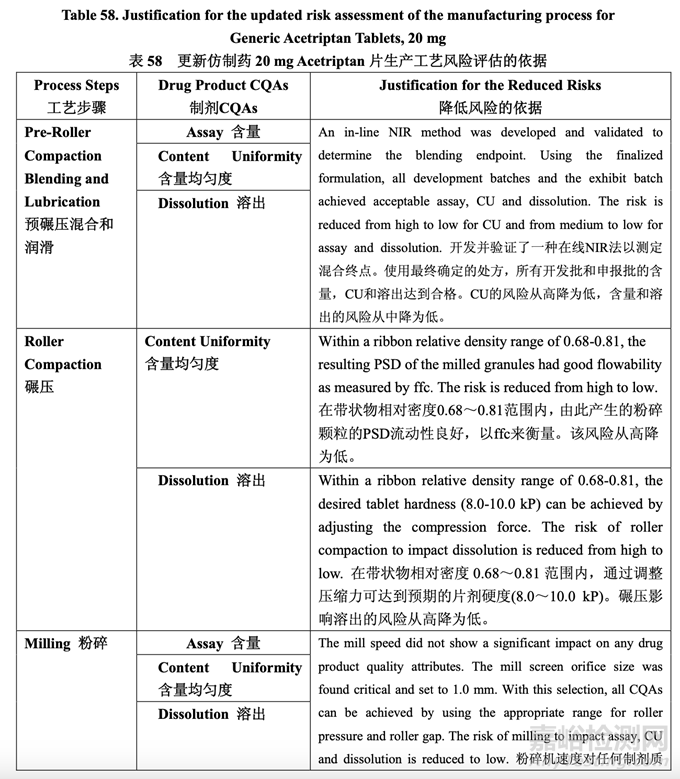
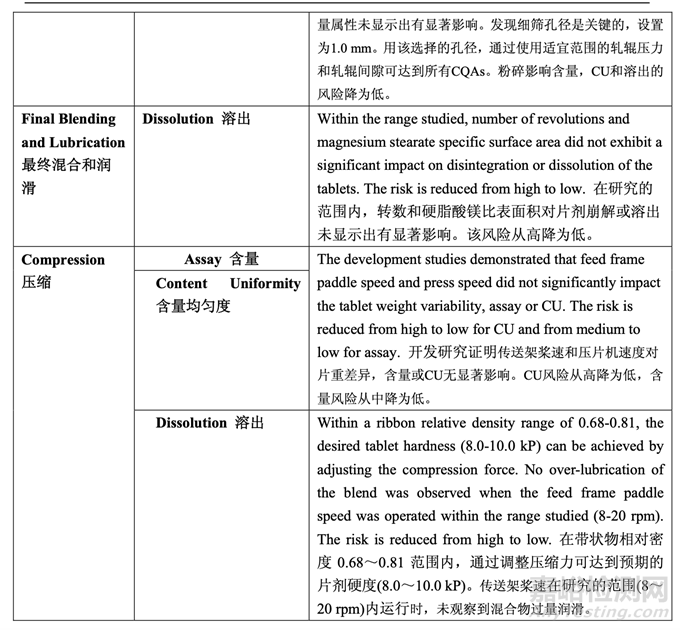
During process development, the identified high risks for each process step were addressed. Experimental studies were defined and executed in order to establish additional scientific knowledge and understanding, to allow appropriate controls to be developed and implemented, and to reduce the risk to an acceptable level. After detailed experimentation, the initial manufacturing process risk assessment was updated in line with the current process understanding. Table 57 presents how the application of the control strategy to the manufacturing process has reduced the identified risks. Table 58 provides the justification for the reduced risk following process development.
工藝開發(fā)中����,討論了每個工藝步驟確定的高風(fēng)險。確定并執(zhí)行了實驗性研究以便建立更多的 科學(xué)知識和理解�,允許適宜的控制以便開發(fā)和執(zhí)行,并將風(fēng)險降低至可接受水平�。在具體的 實驗后��,按照目前的工藝?yán)斫?�,更新了初始生產(chǎn)工藝風(fēng)險評估��。表 57 呈現(xiàn)了用于生產(chǎn)工藝 的控制策略怎樣降低確定的風(fēng)險��。表 58 提供了降低如下工藝開發(fā)風(fēng)險的依據(jù)��。
2.4 Container Closure System
容器密封系統(tǒng)
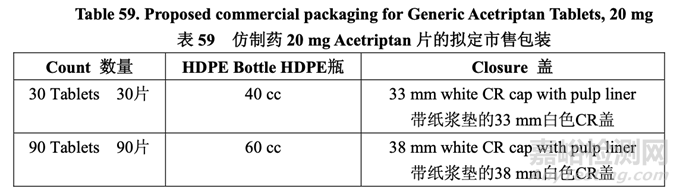
To be consistent with the RLD, the proposed generic drug product is intended to be labeled for storage at 25 °C (77 °F) with excursions permitted to 15-30 °C (59-86 °F). The innovator has chosen round white opaque HDPE bottles with an induction seal liner and child resistant (CR) closure. Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, will be similarly packaged and the bottle pack details are summarized in Table 59.
為與 RLD 一致����,擬定的仿制藥制劑����,擬用標(biāo)簽標(biāo)示貯存在 25 °C (77 °F),允許在 15~30 °C (59~86 °F)內(nèi)偏離����。原研藥選擇圓形白色不透明 HDPE 瓶,并帶有感應(yīng)密封墊和兒童安全(CR) 蓋����。仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片將有類似的包裝,表 59 總結(jié)了具體的瓶包裝信息��。
2.5 Microbiological Attributes 微生物屬性
An accelerated stability study of the exhibit batch demonstrated that the drug product has low water activity and is not capable of supporting microbial growth. Routine microbiological testing of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, is unnecessary due to the low water activity of the product and controls on incoming raw materials. 申報批的加速穩(wěn)定性研究顯示制劑的水分活度低,不能支持微生物生長��。仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的常規(guī)微生物檢測是不必要的由于產(chǎn)品具有低水分活度和控制原材料的措施��。
2.6 Compatibility 相容性
This section is not applicable because the drug product is a solid oral dosage form and there are no reconstitution diluents.
本節(jié)不適用因為制劑是固體口服劑型����,無復(fù)溶稀釋劑。
2.7 Control Strategy 控制策略
Note to Reader: The control strategy is “a planned set of controls, derived from current product and process understanding, that assures process performance and product quality. The controls can include parameters and attributes related to drug substance and drug product materials and components, facility and equipment operating conditions, in-process controls, finished product specifications, and the associated methods and frequency of monitoring and control.”17 致讀者:控制策略是“一系列計劃的控制措施��,來源于目前的產(chǎn)品和工藝?yán)斫?�,確保工藝性 能和產(chǎn)品質(zhì)量��??刂拼胧┛砂ㄅc原料藥和制劑物料和組分����,設(shè)備和設(shè)施的運行條件,在線 控制����,成品質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn),和相關(guān)的方法和監(jiān)測和控制頻率相關(guān)的參數(shù)和屬性��。”
The control strategy for Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, is built upon the outcome of extensive product and process understanding studies. These studies investigated the material attributes and process parameters that were deemed high risk to the CQAs of the drug product during the initial risk assessment. In some cases, variables considered medium risk were also investigated. Through these systematic studies, the CMAs and CPPs were identified and the acceptable operating ranges were established. All variables ranked as high risk in the initial risk assessment are included in
the control strategy because the conclusion of the experiments was dependant on the range(s) studied and the complex multivariate relationship between variables. Thus, the control strategy is an integrated overview of how quality is assured based on current process and product knowledge. The control strategy may be further refined based on additional experience gained during the commercial lifecycle of the product. However, any post-approval changes should be reported to the agency in accordance with CFR 314.70 and should follow steps as outlined by guidances used for scale-up and post-approval changes.
仿制藥20 mg Acetriptan片的控制策略是基于廣泛的產(chǎn)品和工藝?yán)斫庋芯康慕Y(jié)果。這些研究調(diào) 查了被視為初始風(fēng)險評估中制劑CQAs的高風(fēng)險的物質(zhì)屬性和工藝參數(shù)����。在某些情況下,也 調(diào)查了視為中風(fēng)險的變量��。通過這些系統(tǒng)研究�,確定了CMAs和CPPs并確定了可接受的運行 范圍??刂撇呗园怂谐跏硷L(fēng)險評估中列為高風(fēng)險的變量,因為實驗的結(jié)論取決于研究 范圍和變量間的復(fù)雜多元關(guān)系�。因此,控制策略綜合概述了基于目前的工藝和產(chǎn)品知識��,怎 樣保障質(zhì)量����。基于在產(chǎn)品的商業(yè)生命周期中得到的額外經(jīng)驗�,可進一步簡化控制策略。但是��, 根據(jù)CFR 314.70��,任何批準(zhǔn)后的變更應(yīng)報告給專業(yè)的行政結(jié)構(gòu),并應(yīng)遵循如用于放大和批準(zhǔn) 后變更的指南所概述的步驟�。
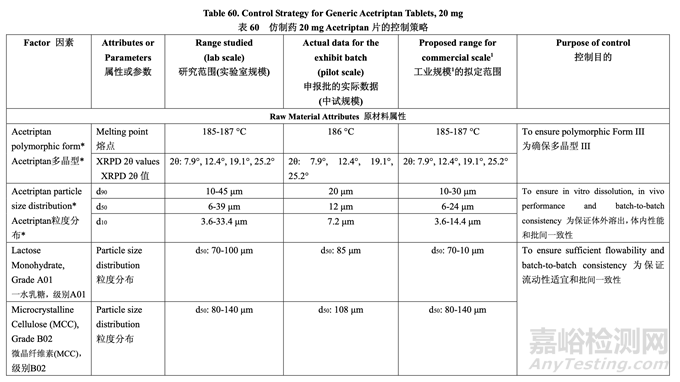
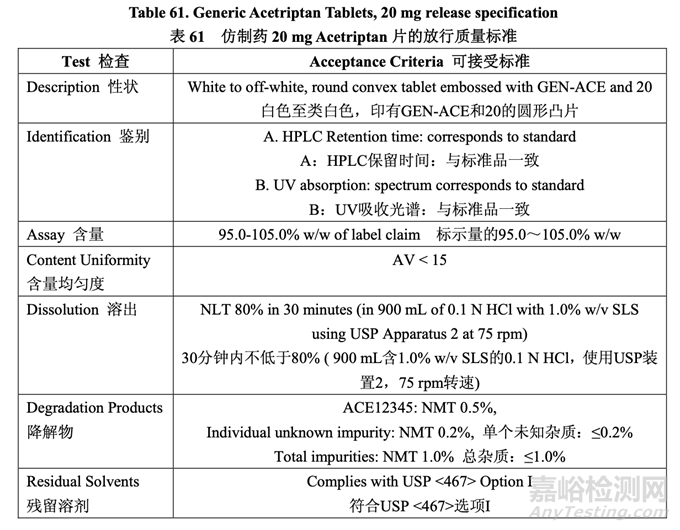
The control strategy for the commercial manufacture of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, is proposed and presented in Table 60. The control strategy includes acetriptan and excipient material attributes to be controlled, in-process controls, high risk process parameter ranges studied during development and the proposed operating ranges for commercial manufacture. The purpose of the controls is also briefly discussed. The release specification for the final product is provided in Table 61.
擬定了仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片工業(yè)生產(chǎn)的控制策略,見表 60��??刂撇呗园刂?acetriptan 和輔料的物料屬性,在線控制措施����,在開發(fā)中研究高風(fēng)險工藝參數(shù)范圍和擬定工業(yè)生產(chǎn)的運 行范圍。也簡要討論了控制措施的目的����。最終產(chǎn)品的放行質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)見表 61。
2.7.1 Control Strategy for Raw Material Attributes 原材料屬性的控制策略
The drug substance particle size distribution limits arise from a combination of its impact on blending and in vivo performance. The pilot PK study suggested that Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, with a drug substance d90 of 30 μm (d50 of 24 μm) or less would be bioequivalent to the RLD. During formulation development, a particle size distribution with a d90 value greater than 14 μm was found to ensure good flow and content uniformity using a fixed blending process. However, implementing a validated in-line NIR method to determine the blending endpoint during process development allowed acceptable blending uniformity and tablet CQAs to be achieved using a drug substance d90 in the range of 10-30 μm.
原料藥粒度分布限度由其對混合和體內(nèi)性能的影響組合而產(chǎn)生�。中試PK研究表明仿制藥20 mg Acetriptan片,用d90為30 μm (d50為24 μm)或以下的原料藥����,將生物等效于RLD。處方開 發(fā)中�,發(fā)現(xiàn)粒度分布的d90值應(yīng)大于14 μm以保證使用固定混合工藝的流動性和含量均勻度良 好。但是��,工藝開發(fā)中實施了經(jīng)驗證的在線NIR法來判斷混合終點�,產(chǎn)生的混合均勻度合格, 合格的片劑CQAs將使用d90在10~30 μm范圍內(nèi)的原料藥來達到��。
Excipient particle size distribution specifications were based on the attributes of the selected grades. For lactose and microcrystalline cellulose, an in-house limit is set on d50 to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
輔料粒度分布質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)是基于所選級別的屬性��。對于 乳糖和微晶纖維素����,設(shè)置了d50的內(nèi)部 限度以保證批間一致性。
Based on the analysis of dissolution data collected during formulation development and the results of the pilot PK study, the dissolution medium with 1.0% w/v SLS was more sensitive to product differences than the FDA-recommended method using medium with 2.0% w/v SLS. For thisreason, 1.0% w/v SLS is used in the dissolution medium for the release method in the control strategy.
基于處方開發(fā)中采集的溶出數(shù)據(jù)分析和中試PK研究的結(jié)果�,含1.0% w/v SLS的溶出介質(zhì)對 產(chǎn)品差異較使用FDA推薦的方法,即含2.0% w/v SLS的介質(zhì)更敏感��?�;谶@個原因�,在控制 策略的釋放方法中,使用含1.0% w/v SLS的溶出介質(zhì)��。
2.7.2 Control Strategy for Pre-Roller Compaction Blending and Lubrication
預(yù)碾壓混合和潤滑的控制策略
The updated risk assessment (Table 37) for the pre-roller compaction blending and lubrication process step demonstrates that the identified risks to blend uniformity have been reduced by adjusting the number of revolutions to accommodate different acetriptan particle size distributions. A validated in-line NIR method for monitoring the blend uniformity was developed, validated and implemented to terminate the blending based on feedback control when the moving block % RSD of ten consecutive spectra is below 5% for ten consecutive measurements. 更新的預(yù)碾壓混合和潤滑工藝步驟的風(fēng)險評估(表37)證明通過調(diào)整轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)以適應(yīng)acetriptan不 同粒度分布可降低確定為混合物均勻度的風(fēng)險�。基于反饋控制����,當(dāng)10個連續(xù)光譜的10個連續(xù) 測量值的移動區(qū)% RSD低于5%時,開發(fā)��,驗證和實施了一種經(jīng)驗證的用于監(jiān)測混合物均勻 度的在線NIR法來終止混合。
2.7.3 Control Strategy for Roller Compaction and Integrated Milling
碾壓和集成粉碎的控制策略
The intent of the control strategy for roller compaction is to maintain the ribbon density within the required range to ensure drug product CQAs are met. To maintain a ribbon relative density of 0.68-0.81 during routine operation, the roller pressure and roller gap will be controlled. The ribbon density will be monitored as an in-process control during roller compaction. 碾壓的控制策略目的是維持帶狀物密度在要求的范圍內(nèi)以保證制劑CQAs符合��。為維持常規(guī) 運行中的帶狀物相對密度在0.68~0.81�,將控制軋輥壓力和軋輥間隙。將監(jiān)測帶狀物密度作 為碾壓中的一種在線控制措施����。
For milling, the mill screen orifice size (1.0 mm) was selected to ensure that the granule size distribution remains within the acceptable range. The acceptable range for mill speed (20-100 rpm) was established and can be adjusted within the range to accommodate different throughput from the roller compaction step. If a change to the mill screen orifice size is made (e.g., increase or decrease) then the impact on granule size distribution and assay of sieve cuts will be reassessed across the pre-defined ribbon density range.
對于粉碎,選擇了細(xì)篩孔徑(1.0 mm)以保證顆粒粒度分布保持在合格范圍內(nèi)��。確定了粉碎機 速度的合格范圍(20~100 rpm)并在范圍內(nèi)進行調(diào)整以適應(yīng)來自碾壓步驟的不同生產(chǎn)量����。如果 變更了細(xì)篩孔徑(如增加或減少),那么在整個預(yù)定義的帶狀物密度范圍內(nèi)�,將重新評估對顆 粒粒度分布和篩分顆粒含量的影響。
2.7.4 Control Strategy for Final Blending and Lubrication 最終混合和潤滑的控制策略
The control strategy for blending the granules with talc is to maintain the targeted number of revolutions. For the granule lubrication with magnesium stearate, the control strategy is to adjust the number of revolutions based on the blender capacity used (headspace) and the volume of the V-blender according to the scientific literature. 顆粒和滑石粉混合的控制策略是維持規(guī)定的目標(biāo)轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)��。對于顆粒與硬脂酸鎂的潤滑�,根據(jù)科 學(xué)文獻,控制策略是調(diào)整轉(zhuǎn)數(shù)����,基于使用的混合機容量(頂空)和V型混合機的容量。
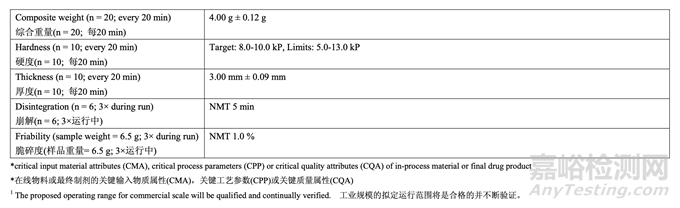
2.7.5 Control Strategy for Tablet Compression 壓片的控制策略
The control strategy for compression is to maintain the in-process tablet attributes of weight, hardness, thickness, friability and disintegration within the required ranges. The fill cam below the die table adjusts the lower punch to the appropriate height to control fill depth and ultimately tablet weight. The target compression force required to produce tablets with the desired hardness, and ultimately friability and disintegration, is established at the beginning of each run. After tablets with the target weight and hardness are obtained during the tablet press set-up, the upper punch penetration depth and the fill depth are fixed. The compression force is continuously measured throughout the run for each tablet and compared to the target compression force. The main compression height is automatically adjusted to keep the average force as close as possible to the target set point. Upper and lower limits of compression force are set and any tablet that registers a compression force outside these limits is automatically rejected by the tablet press.
壓縮的控制策略是維持重量�、硬度�、厚度��、脆碎度和崩解的在線片劑屬性在要求的范圍內(nèi)�。 填料凸輪低于沖臺����,則調(diào)整下沖至適宜的高度以控制填料深度并最終控制片重。在每次運行 的開始確定了可生產(chǎn)出具有預(yù)期硬度并最終具有預(yù)期脆碎度和崩解片劑的目標(biāo)壓縮力��。在壓 片機調(diào)整中得到了具有目標(biāo)重量和硬度的片劑后��,固定上沖穿透深度和填料深度��。這個運行 中連續(xù)測量每片的壓縮力并與目標(biāo)壓縮力比較�。自動調(diào)整主壓縮高度以保持平均力盡可能接 近于目標(biāo)設(shè)定值。設(shè)置壓縮力的上限和下限��,由壓片機自動去除顯示的壓縮力超出這些限度 的任何片劑��。
2.7.6 Product Lifecycle Management and Continual Improvement
產(chǎn)品生命周期管理和持續(xù)改進
Upon approval, the manufacturing process for Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, will be validated using the lifecycle approach that employs risk-based decision making throughout the drug product lifecycle as defined in the FDA process validation guidance.18 經(jīng)批準(zhǔn)����,使用生命周期法來驗證仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的生產(chǎn)工藝,即在整個制劑生命 周期內(nèi)使用如 FDA 工藝驗證指南所定義的基于風(fēng)險的決策����。18
The QbD approach taken during pharmaceutical development of Generic Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg, facilitated product and process understanding relevant to Stage 1 (Process Design) of process validation. During Stage 1, the commercial manufacturing process was defined based on knowledge gained through development and scale up activities and a strategy for process control was developed. The goal of Stage 2 (Process Qualification) is to evaluate if the process is capable of reproducible commercial manufacturing. The manufacturing facility will be designed according to cGMP regulations on Building and Facilities.19 Activities will be taken to demonstrate that utilities and equipment are suitable for their intended use and perform properly. The protocol for process performance qualification will be written, reviewed, approved, and then executed to demonstrate that the commercial manufacturing process performs as expected. The goal of Stage 3 (Continued Process Verification) is continual assurance that the process remains in a state of control (the validated state) during commercial manufacture.
仿制藥 20 mg Acetriptan 片的藥物開發(fā)期間采用的 QbD 法��,有助于理解與工藝驗證階段 1(工 藝設(shè)計)相關(guān)的產(chǎn)品和工藝����。在階段 1 中��,基于從開發(fā)和放大活動中得到的知識�,確定了工 業(yè)生產(chǎn)工藝并開發(fā)了一種工藝控制的策略。階段 2(工藝評定)的目標(biāo)是評估工藝是否能重現(xiàn) 工業(yè)生產(chǎn)�。將根據(jù)關(guān)于建筑和設(shè)備的 cGMP 法規(guī)來設(shè)計生產(chǎn)設(shè)備。19 將采取行動以證明設(shè)施 和設(shè)備適用于其預(yù)期用途并正確操作��。將編寫��,審核��,批準(zhǔn)并執(zhí)行工藝性能確認(rèn)方案以證明 工業(yè)生產(chǎn)工藝如預(yù)期那樣進行��。階段 3(持續(xù)的工藝驗證)的目標(biāo)是持續(xù)保證在工業(yè)生產(chǎn)中����, 工藝保持在控制狀態(tài)(經(jīng)驗證的狀態(tài))。
Throughout the product lifecycle, the manufacturing process performance will be monitored to ensure that it is working as anticipated to deliver the product with desired quality attributes. Process stability and process capability will be measured and evaluated. If any unexpected process variability is detected, appropriate actions will be taken to correct, anticipate, and prevent future problems so that the process remains in control. The additional knowledge gained during routine manufacturing will be utilized for adjustment of process parameters as part of the continual improvement of the drug product. As a commitment, the regulatory agency will be notified in accordance with CFR 314.70 regarding each change in each condition beyond the variability already provided in this application.
整個產(chǎn)品生命周期中��,將監(jiān)測生產(chǎn)工藝性能以確保正在如預(yù)期的那樣工作以提供預(yù)期質(zhì)量屬 性的產(chǎn)品。將測量并評估工藝穩(wěn)定性和工藝能力����。如果檢測到任何非預(yù)期的工藝變異性�,則 將采取適宜的措施以校正,預(yù)期和預(yù)防將來的問題以便工藝保持在控制中��。常規(guī)生產(chǎn)中得到 的額外知識將用于調(diào)整工藝參數(shù)作為制劑持續(xù)改進的一部分�。作為承諾,根據(jù) CFR 314.70 關(guān)于每種情況下的各個變更超過了該申請中已提供的變異性����,將通知監(jiān)管機構(gòu)。
參考文獻:
Example QbD IR Tablet Module 3 Quality 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development�,F(xiàn)DA,2012.