相關(guān)文件:
與驗(yàn)證���、確認(rèn)相關(guān)的主要法規(guī)和標(biāo)準(zhǔn)
1.21CFR PART 820 QUALITY SYSTEM REGULATION.
2.DESIGN CONTROL GUIDANCE FOR MEDICAL DEVICE MANUFACTURERS.
3.ASTM F3172 Standard Guide for Design Verification Device Size and Sample Size Selection for Endovascular Devices.
4.GHTE/SG3/N99-10 Quality Management Systems -Process Validation Guidance
5.GB/T 42061—2022/ISO 13485:2016 醫(yī)療器械 質(zhì)量管理體系 用于法規(guī)的要求
術(shù)語的定義:
Specification規(guī)范
means any requirement with which a product, process, service, or other activity must conform.
產(chǎn)品、過程���、服務(wù)或其他活動(dòng)必須符合的任何要求���。
Validation 確認(rèn)
means confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that the particular requirements for a specific intended use can be consistently fulfilled.
指通過審查和提供客觀證據(jù)來證明特定預(yù)期用途的特殊要求能夠持續(xù)得到滿足。
Process validation 過程確認(rèn)
means establishing by objective evidence that a process consistently produces a result or product meeting its predetermined specifications.
指通過客觀證據(jù)證明過程始終如一地產(chǎn)生符合預(yù)定規(guī)范的結(jié)果或產(chǎn)品�����。
establishment by objective evidence that a process consistently produces a result or device achieving its predetermined requirements.
通過客觀證據(jù)證明過程始終如一地產(chǎn)生符合預(yù)定要求的結(jié)果或器械�����。
Process validation protocol 過程確認(rèn)方案
a document stating how validation will be conducted, including test parameters, product characteristics, manufacturing equipment, and decision points on what constitutes acceptable test results.
說明確認(rèn)將如何實(shí)施的文件���,包括測試參數(shù)���、產(chǎn)品特性���、生產(chǎn)設(shè)備以及測試結(jié)果的接收準(zhǔn)則。
Design validation 設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)
means establishing by objective evidence that device specifications conform with user needs and intended use(s).
指通過客觀證據(jù)證明產(chǎn)品規(guī)范符合用戶需求和預(yù)期用途�����。
establishing by objective evidence that the device conforms to defined user needs and intended use(s).
通過客觀證據(jù)證明器械符合規(guī)定的用戶需求和預(yù)期用途�����。
Verification 驗(yàn)證
means confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that specified requirements have been fulfilled.
指通過審查和提供客觀證據(jù)證明規(guī)定的要求已經(jīng)得到滿足��。
驗(yàn)證
通過提供客觀證據(jù)對(duì)規(guī)定要求已得到滿足的認(rèn)定��。
確認(rèn)
通過提供客觀證據(jù)對(duì)特定的預(yù)期用途或者應(yīng)用要求已得到滿足的認(rèn)定��。
關(guān)鍵工序
指對(duì)產(chǎn)品質(zhì)量起決定性作用的工序��。
特殊過程
指通過檢驗(yàn)和試驗(yàn)難以準(zhǔn)確評(píng)定其質(zhì)量的過程�����。
法規(guī)的要求:
Design verification 設(shè)計(jì)驗(yàn)證
Each manufacturer shall establish and maintain procedures for verifying the device design.
每個(gè)制造商應(yīng)建立和維護(hù)驗(yàn)證器械設(shè)計(jì)的程序���。
Design verification shall confirm that the design output meets the design input requirements.
設(shè)計(jì)驗(yàn)證應(yīng)證明設(shè)計(jì)輸出滿足設(shè)計(jì)輸入的要求�����。
The results of the design verification, including identification of the design, method(s), the date, and the individual(s) performing the verification, shall be documented in the DHF.
設(shè)計(jì)驗(yàn)證的結(jié)果���,包括設(shè)計(jì)的識(shí)別、方法�����、日期和執(zhí)行驗(yàn)證的人員�����,應(yīng)記錄在DHF中��。
confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that the device design (design output) fulfills the specified requirements (design input).
通過審查和提供客觀證據(jù)證明器械設(shè)計(jì)(設(shè)計(jì)輸出)滿足規(guī)定的要求(設(shè)計(jì)輸入)�����。
為確保設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)輸出滿足設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)輸人的要求, 應(yīng)依據(jù)所策劃并形成文件的安排對(duì)設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證���。(GB/T 42061 / ISO 13485)
企業(yè)應(yīng)當(dāng)對(duì)設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證��,以確保設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)輸出滿足輸入的要求�����,并保持驗(yàn)證結(jié)果和任何必要措施的記錄�����。(醫(yī)療器械生產(chǎn)質(zhì)量管理規(guī)范)
Design validation 設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)
Each manufacturer shall establish and maintain procedures for validating the device design.
每個(gè)制造商應(yīng)建立和維護(hù)確認(rèn)器械設(shè)計(jì)的程序��。
Design validation shall be performed under defined operating conditions on initial production units, lots, or batches, or their equivalents.
設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)應(yīng)在規(guī)定的操作條件下對(duì)初始生產(chǎn)單元��、批次��、批次或其等同物進(jìn)行��。
Design validation shall ensure that devices conform to defined user needs and intended uses and shall include testing of production units under actual or simulated use conditions.
設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)應(yīng)確保器械符合規(guī)定的用戶需求和預(yù)期用途���,并應(yīng)包括在實(shí)際或模擬使用條件下對(duì)生產(chǎn)單元的測試�����。
Design validation shall include software validation and risk analysis, where appropriate.
適當(dāng)時(shí),設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)應(yīng)包括軟件確認(rèn)和風(fēng)險(xiǎn)分析���。
The results of the design validation, including identification of the design, method(s), the date, and the individual(s) performing the validation, shall be documented in the DHF.
設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn)的結(jié)果�����,包括設(shè)計(jì)的識(shí)別�����、方法�����、日期和執(zhí)行確認(rèn)的人員��,應(yīng)記錄在DHF中��。
為確保形成的產(chǎn)品能夠滿足規(guī)定的應(yīng)用要求或預(yù)期用途�����,應(yīng)依據(jù)策劃并形成文件的安排對(duì)設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)進(jìn)行確認(rèn)���。(GB/T 42061 / ISO 13485)
企業(yè)應(yīng)當(dāng)對(duì)設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)進(jìn)行確認(rèn)�����,以確保產(chǎn)品滿足規(guī)定的使用要求或者預(yù)期用途的要求���,并保持確認(rèn)結(jié)果和任何必要措施的記錄��。(醫(yī)療器械生產(chǎn)質(zhì)量管理規(guī)范)
Process validation 過程確認(rèn)
Where the results of a process cannot be fully verified by subsequent inspection and test, the process shall be validated with a high degree of assurance and approved according to established procedures. The validation activities and results, including the date and signature of the individual(s) approving the validation and where appropriate the major equipment validated, shall be documented.
如果一個(gè)過程的結(jié)果不能通過后續(xù)的檢查和測試得到充分的驗(yàn)證�����,則該過程應(yīng)進(jìn)行高度保證的確認(rèn)�����,并按照既定的程序進(jìn)行批準(zhǔn)���。確認(rèn)活動(dòng)和結(jié)果,包括批準(zhǔn)確認(rèn)的人員的日期和簽名�����,以及在適當(dāng)?shù)那闆r下對(duì)已確認(rèn)的主要設(shè)備�����,應(yīng)形成文件���。
Each manufacturer shall establish and maintain procedures for monitoring and control of process parameters for validated processes to ensure that the specified requirements continue to be met.
每個(gè)制造商應(yīng)建立并保持經(jīng)過程確認(rèn)的工藝參數(shù)進(jìn)行監(jiān)視和控制的程序�����,以確保持續(xù)滿足規(guī)定的要求���。
設(shè)計(jì)評(píng)審、驗(yàn)證與確認(rèn)的關(guān)系:
In practice, design review, verification, and validation overlap one another, and the relationship among them may be confusing. As a general rule, the sequence is: verification, review, validation, review.
在實(shí)踐中�����,設(shè)計(jì)評(píng)審�����、驗(yàn)證和確認(rèn)是相互重疊的���,并且它們之間的關(guān)系可能是令人困惑的�����。一般來說���,順序是:驗(yàn)證、評(píng)審、確認(rèn)�����、評(píng)審���。
Verification and validation are associated concepts with very important differences.Various organizations have different definitions for these terms. Medical device manufacturers are encouraged to use the terminology of the quality system requirements in their internal procedures.
驗(yàn)證和確認(rèn)是具有非常重大差異又相關(guān)聯(lián)的概念���。不同的組織對(duì)這些術(shù)語有不同的定義。鼓勵(lì)醫(yī)療器械制造商在其內(nèi)部程序中使用質(zhì)量體系要求的術(shù)語�����。
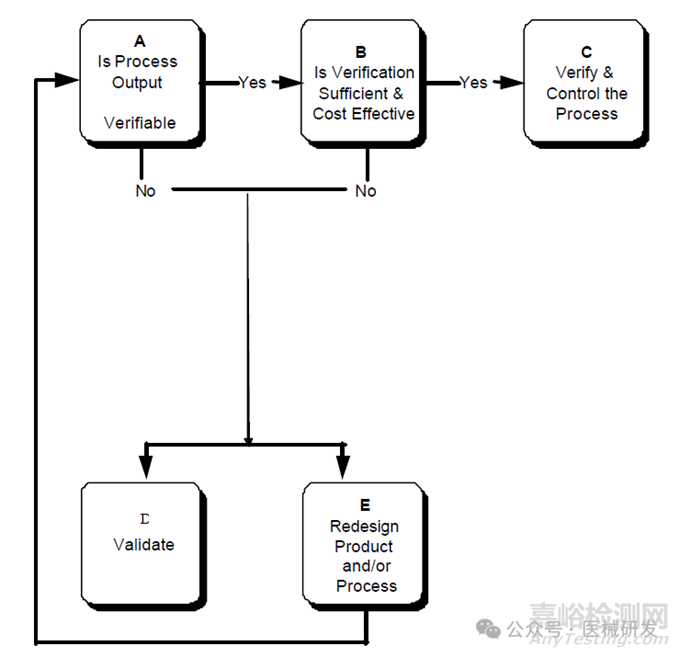
過程確認(rèn)決策樹:
Process validation decision tree過程確認(rèn)決策樹
Each process should have a specification describing both the process parameters and the output desired. The manufacturer should consider whether the output can be verified by subsequent monitoring or measurement (A). If the answer is positive, then the consideration should be made as to whether or not verification alone is sufficient to eliminate unacceptable risk and is a cost effective solution (B). If yes, the output should be verified and the process should be appropriately controlled (C).
每個(gè)過程都應(yīng)該有一個(gè)描述過程參數(shù)和期望輸出的規(guī)范�����。制造商應(yīng)考慮輸出是否可以通過后續(xù)的監(jiān)視或測量進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證(A)�����。如果答案是肯定的��,則應(yīng)考慮單獨(dú)驗(yàn)證是否足以消除不可接受的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)��,并且是一種具有成本效益的解決方案(B)。如果是���,則應(yīng)驗(yàn)證輸出并對(duì)過程進(jìn)行適當(dāng)控制(C)���。
If the output of the process is not verifiable then the decision should be to validate the process (D); alternatively, it may become apparent that the product or process should be redesigned to reduce variation and improve the product or process (E). Also, a change in a manufacturing process may result in the need for process validation even though the process formerly only required verification and control.
如果過程的輸出是不可驗(yàn)證的�����,那么應(yīng)該決定對(duì)該過程進(jìn)行確認(rèn)(D)��;或者��,該產(chǎn)品或工藝很顯然地應(yīng)該重新設(shè)計(jì)以減少變化并改進(jìn)產(chǎn)品或工藝(E)���。此外��,生產(chǎn)工藝的變化可能導(dǎo)致需要做過程確認(rèn)�����,即使該工藝以前只需要驗(yàn)證和控制��。
驗(yàn)證與確認(rèn)總結(jié):
確認(rèn):是從用戶的角度或者能夠是模擬用戶角度來驗(yàn)證產(chǎn)品是否和客戶想要的一致�����;
驗(yàn)證:是從開發(fā)方的角度來做評(píng)審��、測試來驗(yàn)證產(chǎn)品的需求�����、架構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì)等方面是否和輸入要求的一致��;
在開發(fā)階段有:
○ 設(shè)計(jì)驗(yàn)證:確保設(shè)計(jì)和開發(fā)輸出滿足輸入的要求
○ 設(shè)計(jì)確認(rèn):確保產(chǎn)品滿足規(guī)定的使用要求或者預(yù)期用途的要求
為滿足設(shè)計(jì)轉(zhuǎn)生產(chǎn)的需求有:
○ 工藝驗(yàn)證:對(duì)關(guān)鍵工序做驗(yàn)證
○ 過程確認(rèn):對(duì)特殊過程做確認(rèn)
進(jìn)一步的理解:
● 驗(yàn)證針對(duì)的是結(jié)果��,確認(rèn)針對(duì)的是過程��;
● 驗(yàn)證采取的方法通常是試驗(yàn)法��,確認(rèn)采取的是系統(tǒng)的方法��;
● 驗(yàn)證的結(jié)果是證實(shí)被試驗(yàn)的對(duì)象在某一條件下符合規(guī)定的要求���。確認(rèn)的結(jié)果是證實(shí)運(yùn)用該過程可以在某個(gè)范圍內(nèi)持續(xù)產(chǎn)出符合要求的輸出��;
● 驗(yàn)證要保證“做得正確”�����,確認(rèn)則要保證“做的東西有用”��;
● 驗(yàn)證注重“過程”���,確認(rèn)注重“結(jié)果”��;
● 驗(yàn)證是自我視角�����,確認(rèn)是客戶視角;
● “驗(yàn)證”是要證明我們“做好”產(chǎn)品���,“確認(rèn)”是要證明我們“做的產(chǎn)品好”���;